
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
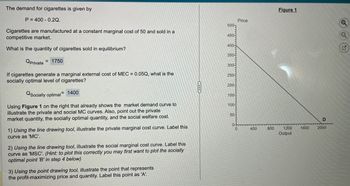
Transcribed Image Text:The demand for cigarettes is given by
P 400 0.2Q.
Cigarettes are manufactured at a constant marginal cost of 50 and sold in a
competitive market.
What is the quantity of cigarettes sold in equilibrium?
Qprivate
= 1750
Price
500
450-
400-
350-
300-
250-
200-
150-
100
If cigarettes generate a marginal external cost of MEC = 0.05Q, what is the
socially optimal level of cigarettes?
QSocially optimal 1400
Using Figure 1 on the right that already shows the market demand curve to
illustrate the private and social MC curves. Also, point out the private
market quantity, the socially optimal quantity, and the social welfare cost.
1) Using the line drawing tool, illustrate the private marginal cost curve. Label this
curve as 'MC'.
2) Using the line drawing tool, illustrate the social marginal cost curve. Label this
curve as 'MSC'. (Hint: to plot this correctly you may first want to plot the socially
optimal point 'B' in step 4 below)
3) Using the point drawing tool, illustrate the point that represents
the profit-maximizing price and quantity. Label this point as 'A'.
50-
Figure 1
D
0
400
800
1200
1600
2000
Output
G
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The production Compact Fluorescent Lightbulbs (CFL) use mercury in their production process. Mercury is a heavy metal and considered bad for the environment. Suppose the marginal external cost is $5 per lightbulb and the government levies a corrective tax of $5.50 per lightbulb. With this new tax: Selected answer will be automatically saved. For keyboard navigation, press up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a b Question 4 с d The price will be below the marginal social cost. Not enough light bulbs will be produced. The price will be below the marginal social benefit. The price will be below the marginal cost to produce light bulbs.arrow_forwardPlease give detailed procedurearrow_forwardSuppose that a local airport is near a residential neighborhood. To land at this airport, an airliner must pay $51. To soundproof the local homes, so residents do not hear airplanes all hours of the day, residents must pay $28. What is the private cost for a plane to land at this airport? What is the external cost of a plane landing at the airport? What is the social cost of a plane landing at the airport? F11 F12 F5 F6 F8 F9 F10 F7 F2 F3 F4 prt sarrow_forward
- The figure below shows the market for a chemical, of which the production causes certain negative externalities in the form of pollution. Define MCP = marginal private cost, MCS = marginal social cost, D = market demand, P = price, and Q = quantity. 4 10 (a) (b) (c) (d) 100 P MC, ML D If the market is competitive, what is the equilibrium price and quantity? Is this equilibrium outcome socially optimal? In terms of the areas denoted by A, B, and C, what is the deadweight loss to society if the market is competitive? What can the government do to achieve the socially optimal level of pollution?arrow_forward2) Suppose the demand curve for a rubber-based product is Q_D=225-0.5P, and the supply curve is Q_S=0.5P-15. If the external cost of the suit from the waste produced by the factory producing the item is MEC-Q, calculate: (a) Competitive price and quantity when there is no control over the waste disposal of the factory. (b) Price and quantity at the socially optimal level.arrow_forwardBN12.2 (a) Case: The market for dry cleaning is reflected by the demand and supply curves (Q is in thousands): Pa = 5-Q Ps= 2+2Q Producing dry cleaning creates ground water pollution with a constant marginal external cost of 1.2. Question: (a) Sketch a graph that shows the Dsoc, Spriv, Ssoc, Qopt (societal perspective) and DWL in an unregulated market (No need to label the values in the graph)?arrow_forward
- 2. Suppose that demand for a product is Q = 1200 - 4P and supply is Q = -240 +2 P. Furthermore, suppose that the marginal external damage of this product is $12 per unit. How many more units of this product will the free market produce than is socially optimal? Calculate the deadweight loss associated with the externality.arrow_forwardOnly typed answer You are an industry analyst that specializes in an industry where the market inverse demand is P = 100 - 3Q. The external marginal cost of producing the product is MCExternal = 6Q, and the internal cost is MCInternal = 14Q. Instruction: Round your answers to the nearest two decimal places. a. What is the socially efficient level of output? units b. Given these costs and market demand, how much output would a competitive industry produce? units c. Given these costs and market demand, how much output would a monopolist produce? units d. Which of the following are actions the government could take to induce firms in this industry to produce the socially efficient level of output. Instructions: You may select more than one answer. Click the box with a check mark for the correct answers and click twice to empty the box for the wrong answers. You must click to select or deselect each option in order to receive full credit. Pollution taxes…arrow_forwardThe supply and demand of sugar are given as Qs = 5P, Qd = 250- P where Qs is tons supplied per year, P is the price per ton; Qd is tons demanded per year. Because of the pollution associated with production, marginal external costs of 40 are associated with each ton of sugar. Assuming that sugar is sold in a competitive market, What is the market price? How many tons of paper will be produced per year at that price? What is the efficient output of paper? What is the amount of total Pigouvian tax to achieve efficiency? What is the amount of total Pigouvian subsidy to achieve efficiency?arrow_forward
- Consider a market where the demand curve is given by P = 190 – 0.2Q and the supply curve is given by P = 41 + 0.1Q. Production of this good generates an external cost as measured by the marginal external cost function MEC = 0.1Q. If the government wants to encourage firms to produce at the socially efficient level of output then how large should the per unit tax be? Enter a number rounded to two decimal places as necessaryarrow_forwarddo fastarrow_forwardSuppose the demand for a product is P = 400 - 0.25 Q and the supply of the product is P = 100 +0.75 P where Q is output and P is price. Suppose also that the marginal external cost (MEC) from production is constant and equal to 50$ per unit. What is the competitive (private) efficient level of output? What is the socially efficient level of output?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education