
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
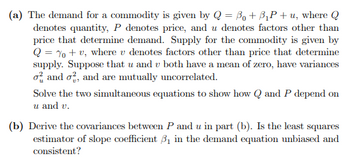
Transcribed Image Text:(a) The demand for a commodity is given by Q = Bo + B₁P+u, where Q
denotes quantity, P denotes price, and u denotes factors other than
price that determine demand. Supply for the commodity is given by
Q = % + v, where v denotes factors other than price that determine
supply. Suppose that u and u both have a mean of zero, have variances
o and o2, and are mutually uncorrelated.
Solve the two simultaneous equations to show how Q and P depend on
u and v.
(b) Derive the covariances between P and u in part (b). Is the least squares
estimator of slope coefficient 3₁ in the demand equation unbiased and
consistent?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Two identically able agents are competing for a promotion. The promotion is awarded on the basis of output (whomever has the highest output, gets the promotion). Because there are only two workers competing for one prize, the losing prize=0 and the winning prize =P. The output for each agent is equal to his or her effort level times a productivity parameter (d). (i.e. Q2=dE1 , Q2=dE2). If the distribution of “relative luck” is uniform, the probability of winning the promotion for agent 1 will be a function of his effort (E1) and the effort level of Agent 2 (E2). The formula is given by...Prob(win)=0.5 + α(E1-E2), where α is a parameter that reflects uncertainty and errors in measurement. High measurement errors are associated with small values of α (think about this: if there are high measurement errors, then the level of an agent’s effort will have a smaller effect on his/her chances of winning). Using this information, please answer the following questions. Both workers have a…arrow_forwardStatic Bayesian Games] We consider a games with 2 players. Player 1 has only asingle type; however, Player 2 can have two types I and D, each with probability 50%. Bothplayers have two actions available to them. The game has the following payoffs (P1 is the rowplayer, P2 the column player):arrow_forwardWhich distribution is a probability distribution with a low mean and highly skewed to the right? Which distribution is a probability distribution with a low mean and highly skewed to the right? Level distribution Normal distribution Poisson distribution Uniform distributionarrow_forward
- ii) Suppose that you find out that you have an OLS estimator which is unbiased but has a non-minimum variance. Discuss two practical steps that you take to reduce the variance of your OLS estimator. Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardConsider a class with 80 enrolled students. None of the students were ill at the beginning of the school year. On August 30th, 10 students reported having a common cold. All continued to be ill on September 1st, but all 10 recovered within 3 days. On September 15th, 5 more students had a cold. All of these students continued to be ill on September 16th, but all recovered 5 days later. In this example, assume that a person cannot have a cold more than once.calculate the cumulative incidence of the common cold in the class during the month of septemberarrow_forwardIn a hypothetical country called Tritonland, demand and supply of fish are determined by the following system of equations: Q Q = 3+P+v, where Q and P stand for quantity and price respectively, and that u and v are independent Uniform [0, 2]. Suppose we have i.i.d. observations (Qi, Pi)_1 from n markets in equilibrium. Answer the next few questions. = 15 P+u,arrow_forward
- Econometrics Thomas Eisensee and David Stromberg wanted to measure how much news coverage of a foreign disaster impacted the amount of disaster relief provided by the U.S. government. They argue that the simple relationship would be biased. Let X = Minutes of News Coverage and Y= Disaster Aid. Choose a variable X2 that could bias the simple relationship. This variable should impact the amount of coverage and impact the amount of aid for reasons other than purely news coverage. Eisensee and Stromberg introduce an instrument Z = During the Olympics. Explain how Z could satisfy the relevant and exogenous criteria. Explain how you could use Z to estimate the impact of X on Y free from X2 bias. Hint: you should mention two stages.arrow_forwardThis problem involves empirical probability. The table shows the breakdown of 95 thousand single parents on active duty in the U.S. military in a certain year. All numbers are in thousands and rounded to the nearest thousand. Use the data in the table to find the probability that a randomly selected single parent in the U.S. military is in the Army. Male Female Total Army 24 10 34 Navy 27 8 35 Marine Corps 5 1 6 Air Force 146 20 Total 70 25 95 The probability that a randomly selected single parent in the U.S. military is in the Army is (Type an integer or decimal rounded to the nearest hundredth as needed.)arrow_forwardThe lowest boundary of the model class with size 15 is 40.the frequency of this class is 7 .find the mode if frequencies of the classes preceding and succeeding the model class is 3 and 6 respectivelyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education