
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134753119
Author: Sheldon Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
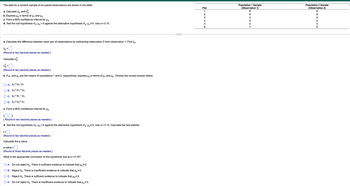
Transcribed Image Text:The data for a random sample of six paired observations are shown in the table.
a. Calculate X and s².
S
b. Express μ in terms of H₁ and
H₂.
c. Form a 90% confidence interval for μd.
d. Test the null hypothesis Ho: μ = 0 against the alternative hypothesis H₂: µå ‡0. Use α = 0.10.
a. Calculate the difference between each pair of observations by subtracting observation 2 from observation 1. Find Xd.
Xd=
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Calculate s
2
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
b. If μ₁ and μ₂ are the means of populations 1 and 2, respectively, express μ in terms of μ₁ and µμ2. Choose the correct answer below.
A. Hd=H₂ H₁
B. Hd1₁H₂
OC. Hd H₁-H₂
O D. Hd=H₂ + H₂
c. Form a 90% confidence interval for μd.
(00)
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
d. Test the null hypothesis Ho: μ = 0 against the alternative hypothesis H₂: Hd #0. Use α = 0.10. Calculate the test statistic.
t=
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Calculate the p-value.
p-value=
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
What is the appropriate conclusion of the hypothesis test at α = 0.10?
O A. Do not reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to indicate that μ‡0.
B. Reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence to indicate that μg 0.
O C. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to indicate that μ‡0.
O D. Do not reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence to indicate that Hd
#0.
Pair
1
23456
Population 1 Sample
(Observation 1)
663647
Population 2 Sample
(Observation 2)
8
9
4
6
5
6
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step 1: Given information:
VIEW Step 2: Calculate sample mean and sample variance for difference:
VIEW Step 3: Choose correction answer:
VIEW Step 4: Calculate 90% confidence interval for true mean difference:
VIEW Step 5: Set hypothesis and Calculate t-statistic:
VIEW Step 6: Calculate p-value:
VIEW Step 7: Conclusion:
VIEW Solution
VIEW Step by stepSolved in 8 steps with 46 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Do question 7,8 and 9 only The new study also carried out a test to determine whether the population proportion of unvaccinated school children contracting winter flu was higher than the population proportion of vaccinated school children. The Z test statistic to test this belief is found to be 1.874. The corresponding p-value is 0.0305 0.1212 0.3036 0.7724 Question 7 Suppose that the new study uses a level of significance of 0.05 to test the claim in Question 6. The probability of Type I error is 0.025 0.05 0.95 0.975 Question 8 Based on previous studies of school children who were vaccinated and contracted the flu, the time in hours that the flu symptoms last is assumed to follow a normal distribution with a mean of 20.7 hours and a standard deviation of 7.3 hours. The probability that a randomly selected school child has flu symptoms for more than 24 hours is 0.1628 0.3256 0.6744 0.8372 Question 9 Suppose that a random sample of 5 vaccinated school children is taken. Assuming the…arrow_forwardMolly works for a meat producer, and she needs to determine whether containers of ground beef have the correct fat content. She obtains a random sample of 120 containers of ground beef and finds that 84 percent have the correct fat content. Molly then conducts a hypothesis test of H0:p=0.80H0:p=0.80 versus Ha:p≠0.80Ha:p≠0.80 and calculates a test statistic of 1.10 with a pp-value of 0.273. Which of the following best represents the meaning of the pp-value? If the population proportion is 0.84, the probability of observing a sample proportion of 0.80 is 0.273. A If the population proportion is 0.84, the probability of observing a sample proportion of at least 0.04 less than 0.84 is 0.273. B If the population proportion is 0.80, the probability of observing a sample proportion within 0.04 of 0.80 is 0.273. C If the population proportion is 0.80, the probability of observing a sample proportion at least 0.04 greater than 0.80 is 0.273. D If the…arrow_forwardGiven two independent random samples with the following results: ₁ = 16 n₁ = 8 ₁ = 98 ₁ = 70 s₁ = 15 5 = 19 Use this data to find the 90% confidence interval for the true difference between the population means. Assume that the population variances are equal and that the two populations are normally distributed. Step 3 of 3: Construct the 90% confidence interval. Round your answers to the nearest integer. Copy Dataarrow_forward
- (i) State the hyptheses. (ii) Sketch a scatter plot tat best represents the data. (iii) Compute the value of the correlation coefficient. Round the answer to at least three decimal places. (iv) Find the P-value. Round the answer to at least four decimal places. Test the significance of r at α=0.05. Determine whether to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.arrow_forwardUnder what circumstances is a t statistic used instead of a z-score for a hypothesis test? Justin wants to know whether a commonly prescribed drug does improve the attention span of students with attention deficit disorder (ADD). He knows that the mean attention span for students with ADD who are not taking the drug is 2.3 minutes long. His sample of 12 students taking the drug yielded a mean of 4.6 minutes. Justin can find no information regarding σx , so he calculated s2x =1.96. Determine the critical region using a one-tailed test with alpha = .05. Conduct the hypothesis test (Do the math and compare the t-critical and t-obtained values). State your conclusions in terms of H0 (Should you reject the H0 or fail to reject/accept the H0). Based on your analysis, is there a relationship between the drug and attention span?arrow_forwardYou wish to conduct a hypothesis test to determine if a bivariate data set has a significant correlation among the two variables. That is, you wish to test the claim that there is a correlation (Ha : p ‡ 0). You have a data set with 7 subjects, in which two variables were collected for each subject. You will conduct the test at a significance level of a = 0.05. Find the critical value for this test. rc.v. = ± Report answers accurate to three decimal places.arrow_forward
- . Buck randomly selects 38 basketball shoes from the Shoe Warehouse and finds the mean prie to be $66.88 with a standard deviation of $5.62. Construct a 99% confidence interval for the population standard deviation o, and find the x2 values used in the calculation. A. ($4.31, $7.93) with xỉ = 18.586 and x = 62.833 B. ($4.27, $7.78) with xỉ = 19.286 and xỉ = 64.181 C. ($1.82, $3.34) with xỉ = 18.586 and x = 62.833 D. ($4.27, $7.78) with xỉ = 19.960 and xi = 59.893 E. ($18.58, $62.88) with xỉ = 18.586 and x = 62.833 %3D %3D rejectarrow_forwardFor each effect, state whether the null hypothesis was rejected or not. Calculate the effect size for the effect of stressarrow_forwardGiven two independent random samples with the following results: n₂ = 8 x₂ = 175 $2 = 11 n₁ = 12 x₁ = = 157 $₁ = 32 Use this data to find the 95% confidence interval for the true difference between the population means. Assume that the population variances are not equal and that the two populations are normally distributed. Copy Data Step 1 of 3: Find the critical value that should be used in constructing the confidence interval. Round your answer to three decimal places.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:PEARSON
