
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
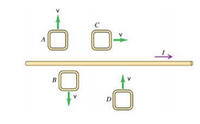
The current I in a long, straight wire is constant and is directed toward the right.
a) Is the direction of the induced current clockwise or counterclockwise, or is the induced current zero for loop D? Briefly explain.
b) What is the direction of the net force that the wire exerts on the loop D? (No explanation is needed.)
c) Is the direction of the induced current clockwise or counterclockwise, or is the induced current zero for loop C? Briefly explain.
Transcribed Image Text:B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A loop of wire carries a current (provided by a battery which is not shown) next to a bar magnet. The magnet is repelled from the loop. Which way does current run in the loop? Cannot determine, we need to know if the flux is changing. Out of the page on the top, Into the page on the bottom. Into the page on the top, Out of the page on the bottom.arrow_forwardThe distance between the wire and the circular current loop is r = 2.4 cm. (Figure 1) Figure O 2.0 A -Wire 0.20 A 1 of 1 2.0 mm What is the magnitude of the torque on the circular current loop? Express your answer with the appropriate units. T = Submit Part B μÀ Value Request Answer Units What is the loop's stable equilibrium position? ? O The dipole will be in equilibrium after rotating clockwise 135°. O The dipole will be in equilibrium after rotating clockwise 180°. O The dipole will be in equilibrium after rotating clockwise 45°. O The dipole will be in equilibrium after rotating clockwise 90°.arrow_forward7. Consider two semi-infinite wires connected with a 4 circular bend and current i flowing as shown. Using an appropriate combination of the Biot-Savart Law dB = Hoi dĩ x ê Ampere's Law 4n r² PB• ds = H, ime > superposition, and symmetry to calculate B at point P as indicated. Note: You must correctly support each step and explain exactly what assumptions you are making. Rarrow_forward
- X R The figure above shows two parallel loops of wire having a common axis. The smaller loop (radius r) is above the larger loop (radius R) by a distance x >> R. Consequently, the magnetic field due to the counterclockwise current i in the larger loop is nearly constant throughout the smaller loop. Suppose that x is increasing at the constant rate dx/dt = V. NOTE: Express your answers to parts (a) and (b) in terms of the given variables. (a) Find an expression for the magnetic flux through the area of the smaller loop as a function of x. ÞB(x) = (b) Determine the magnitude of the induced emf in the smaller loop. E = (c) Determine the direction of the current in the small loop. Choose one ▾arrow_forwardA current loop in a motor has an area of 1.95 cm² . It carries a 240 mA current in a uniform field of 0.62 T. 1 Part A What is the magnitude of the maximum torque on the current loop? Express your answer with the appropriate units. T= BHA μÅ S Value → C Units ?arrow_forwardI There is a straight, infinite current is directed towards the right and a small loop of wire (with the normal to the plane of the loop perpendicular to the current) located as shown. Which of the following would result in no current being induced in the loop? Select one or more: D a. turn off the current o b. move the loop towards the wire D c. move the loop away from the wire o d. move the loop towards the rightarrow_forward
- Two loops carry equal currents I in the same direction. The loops are held in the positions shown in the figure and are then released. Which one of the following statements correctly describes the subsequent behavior of the loops? O The loops remain in the positions shown. O The top loop moves to the right; the bottom loop moves to the right. O The loops attract each other. Both loops move to the left. O The loops repel each other. Carrow_forwardThe component of the external magnetic field along the central axis of a 69 turn circular coil of radius 47.0 cm decreases from 2.90 T to 0.700 T in 2.10 s. If the resistance of the coil is R = 3.00 §, what is the magnitude of the induced current in the coil? magnitude: What is the direction of the current if the axial component of the field points away from the viewer? counter-clockwise clockwise Aarrow_forwardc) Indicate the magnetic poles of the coil, and draw the induced magnetic field and the direction of the induced current. Varrow_forward
- a very long wire in three different ways as shown in the figures. 1 2 The radius of the circular loop is R = 31.3 cm and the wire carries the same electric current I = 18.1 A in all three cases. In the first and in the second case the plane of the circle is parallel to the straight wire segments, in the third case the plane of the circle is perpendicular to the straight segments. The straight segments are very long in all three cases in both directions. What is the size of the magnetic field at the center of the circle in the first case? Submit Answer Tries 0/99 What is the size of the magnetic field at the center of the circle in the second case? Submit Answer Tries 0/99 What is the size of the magnetic field at the center of the circle in the third case? Submit Answer Tries 0/99arrow_forward15barrow_forwardThe horizontal loop in the figure is placed in an external magnetic field B pointing downwards. If the external field B is increasing with time, then what is the direction of the induced current in the loop as viewed from above? t B Choose your answer from: Clockwise / Counterclockwise / No induced currentarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON