
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
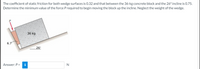
Transcribed Image Text:The coefficient of static friction for both wedge surfaces is 0.32 and that between the 36-kg concrete block and the 26° incline is 0.75.
Determine the minimum value of the force P required to begin moving the block up the incline. Neglect the weight of the wedge.
36 kg
6.7
26°
Answer: P =
i
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 1. Block on Incline Determine whether the block shown is in equilibrium, and find the magnitude and direction of the friction force when = 30° and P = 200 N. impossible Block moves F = 193.2 N/ H, = 0.30 H = 0.20 P I KNarrow_forwardEXERCISE 2.34 The cable, whose length is 300 mm, is fastened to the 500-g block. Clockwise rotation of the arm at a constant angular speed of 5 rad/s causes the block to slide outward. The motion occurs in the vertical plane, and the coefficient of sliding friction is 0.4. Determine the tensile force in the cable and the force exerted by the block on the walls of the groove when = 53.1301⁰. 300 mm -300 mm- (Hint: use polar coordinates to solve the problem. R is from the rotation center of the arm to the block and is as shown in the Figure. Let L be the total length of the cable and S be the length from the clamped end of the cable to the end of the arm.)arrow_forwardWhile digging a small hole prior to planting a tree, a homeowner encounters rocks. If he exerts a horizontal 199-N force on the prybar as shown, what is the horizontal force exerted on rock C? Note that a small ledge on rock C supports a vertical force reaction there. Neglect friction at B. Complete solutions (a) including and (b) excluding the weight of the 23-kg prybar. 199 N 1260 mm 21 190 mm Answers: (a) Including weight, Fc = i N (a) Excluding weight, Fc = i Narrow_forward
- The two 5.0° wedges shown are used to adjust the position of the column under a vertical load Fof 8.7 kN. Determine the magnitude of the forces Prequired to raise the column if the coefficient of friction for all surfaces is 0.36. Assume e = 5.0°. F Answer: P = kNarrow_forwardThe crate pulled by a man as shown weighs 200 N. Supposed that the static friction coefficient between the contact surfaces is 0.25. Determine the following: a.) The value of angle alpha (ᾳ) to obtain the smallest possible value of the pulling force the man exerted so that the crate is on the verge of moving. b.) The smallest value of the pulling force the man exerted, c.) The normal reaction between the contact surfaces (Crate and Horizontal floor).arrow_forwardA 150-lb block rests on a horizontal floor. The coefficient of friction between the block and the floor is 0.30. A pull of 40 lb, acting upward at an angle of 30° to the horizontal, is applied to the block. Determine whether or not the block will slide. - Draw Free-body diagram - Solve most simple way - use the formula Fmax= Ms (N)arrow_forward
- The uniform 6.1-m pole has a mass of 130 kg and is supported as shown. Calculate the force Prequired to move the pole if the coefficient of static friction for each contact location is 0.41. 2.6 m Answer: Pi 646.90 6.1 m $3.6 m B Narrow_forwardThe uniform rod BC weighs 32.2 lb. The rod is connected to the frame D by a frictionless pin C and a cord AB as shown. Calculate the maximum value of the applied force P for which rod BC will not “rise up”.arrow_forwardCould you go step by step on how to solve this problem. I've been tackling it for the past few hours and I can't seem to get it quite right.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY