
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The cleaning ability of soap is based on its structure.
Which structures represent compounds that can be used as soaps?
are the following Soap or Not a Soap.
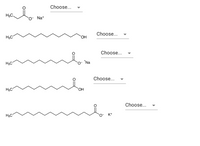
Transcribed Image Text:Choose...
H3C.
Na+
Choose...
H3C
HO.
Choose...
H3C
`o- *Na
Choose...
H3C
HO.
Choose...
H3C
K+
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The monomers of lipids are called fatty acids. Draw the lipid monomer a fatty acid, labeling the hydrocarbon chain and the carboxyl end group. Be sure to show ALL of the atoms within the molecule (there are several different fatty acids in living things including oleic acid and stearic acid, each with a unique molecular formula). Do not give handwriting solution.arrow_forwardClassify the lipid shown here as saturated or unsaturated and determine the number of carbon atoms present.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is true about a soap molecule? The carbon chain is polar and it attracts grease particles, while the carboxylate salt is nonpolar and it attracts water. The carbon chain is nonpolar and it attracts grease particles, while the carboxylate salt is polar and it attracts water. The carbon chain is nonpolar and it attracts water while the carboxylate salt is polar and it attracts grease particles. O Both, carbon chain and carboxylate salt are polar and attract only water.arrow_forward
- Using the given IUPAC name 4-chloro-3,4-dimethylnonan-1-amine Please help with the following: On a page titled Hydrogen Bonding with Water print/draw the expanded structure ofyour molecule. (If the structure already contains any dashed lines, make them solid (nondashed) covalent bonds for this assignment so that they are not confused with hydrogenbonds)o Illustrate all the locations where your molecule could form hydrogen bonds withwater either as a hydrogen donor or as a target (receiver) of hydrogen bonds fromwater. Do this by drawing bent water molecules as necessary and representinghydrogen bonds between water and the molecule using dashed lines. Be sure it isclear exactly which atoms on each molecule are involved in the hydrogen bonds.o If your molecule is not capable of forming hydrogen bonds with water explain whynot. On a page titled Polarity and Solubility Predictions draw/print the structural formula ofyour molecule (expanded or condensed)o Circle or highlight all polar…arrow_forwardFatty acids are molecules with a carboxylic acid on one end and long hydrocarbon chain on the other. The sodium salts of fatty acids (such as sodium strearate, shown below) are commonly used in soaps to trap nonpolar dirt and grease particles. Soap does not work well in "hard water, which is water with high concentration of magensium and calcium ions (often found in water obtained from wells) Explain this observation at a molecular level.arrow_forward13. Cholesterol is considered a Lipid as well even though it does not have a carboxylic acid like Fatty Acids do. For the following structure of cholesterol list the two functional groups on the molecule and state which side of the molecule you think is polar and which is nonpolar ноarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY