
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
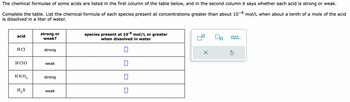
Transcribed Image Text:The chemical formulae of some acids are listed in the first column of the table below, and in the second column it says whether each acid is strong or weak.
Complete the table. List the chemical formula of each species present at concentrations greater than about 10-6 mol/L when about a tenth of a mole of the acid
is dissolved in a liter of water.
acid
H Cl
H CIO
ΗΝΟ,
H₂S
strong or
weak?
strong
weak
strong
weak
species present at 10-6 mol/L or greater
when dissolved in water
0
0
0
☐
X
Ś
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- plese don't handwritten solution..arrow_forwardCalculate either [H3O+] or [OH-] for each of the solutions at 25 °C. Solution A: [OH-] = 2.15 x 10-7 M; [H,₂0*] = Solution B: [H₂O+] = 8.53 x 10-⁹ M; [OH-] = Solution C: [H3O+] = 5.83 x 10-4 M; [OH-] = Which of these solutions are basic at 25 °C? Solution B: [H3O+] = 8.53 × 10-⁹ M Solution C: [H3O+] = 5.83 x 10-4 M Solution A: [OH-] = 2.15 x 10-7 M M M Marrow_forwardWhat salt is formed in the following acid-base reaction? LiOH (aq) + H3PO4 4 (aq) Give the chemical formula, but do not use subscripts. For example, if the answer is Ca3(PO4)2, report your answer as Ca3(PO4)2. If no salt is predicted to form, type in NONE.arrow_forward
- In an aqueous solution, if H+ increases then OH decreases. True O Falsearrow_forwardDetermine the [OH−], pH, and pOH of a solution with a [H+]of 5.7×10−9 M at 25 °C. [OH−]= pH= pOH= Determine the [H+] , pH, and pOH of a solution with an [OH−] of 5.1×10−9 M at 25 °C. [H+]= MM pH= pOH= Determine the [H+] , [OH−] , and pOH of a solution with a pH of 3.063.06 at 25 °C. [H+]= [OH−]= pOH= Determine the [H+][H+] , [OH−][OH−] , and pH of a solution with a pOH of 5.525.52 at 25 °C. [H+]= [OH−]= pH=arrow_forwardThe H⁺ concentration in an aqueous solution at 25 °C is 3.7 × 10⁻⁴. What is [OH⁻]?arrow_forward
- Determine the [OH−] , pH, and pOH of a solution with a [H+] of 0.0096 M at 25 °C.[OH−]= MpH=pOH=Determine the [H+] , pH, and pOH of a solution with an [OH−] of 7.5×10−7 M at 25 °C.[H+]= MpH=pOH=Determine the [H+] , [OH−] , and pOH of a solution with a pH of 12.84 at 25 °C.[H+]= M[OH−]= MpOH=Determine the [H+] , [OH−] , and pH of a solution with a pOH of 4.34 at 25 °C.[H+]= M[OH−]= MpH=arrow_forwardClassify each of the following substances as either a strong or weak acid, strong or weak base, or a soluble or insoluble salt. Clear All strong acid ВаBr, weak acid HI strong base NAOH weak base HCN soluble salt Ba(OH)2 insoluble saltarrow_forwardCalculate the percent ionization of a 0.437 M solution of hypochlorous acid. (Assume that K₁ (HClO) = 3.5 × 10−8.) % lonization = %arrow_forward
- Calculate the hydroxide ion concentration of an aqueous solution of 0.480 M hydrofluoric acid. (Assume that K₂ (HF) = 7.2 × 10−4.) [OH] =| Marrow_forwardThe H⁺ concentration in an aqueous solution at 25 °C is 4.5 × 10⁻⁴. What is [OH⁻]?arrow_forwardEach value represents a different aqueous solution at 25 °C. Classify each solution as an acid, base, or neutral. [OH−]= 3.0 × 10 − 6 [H+]= 8.1 × 10 − 13 pOH= 13.67 pOH= 7.00 [H+]= 5.3 × 10 − 3 [OH-]= 3.0x 10^-6 is a(n) Question Blank 1 of 5 , [H+]= 8.1 x 10^-13 is a(n) Question Blank 2 of 5 , pOH= 13.67 is a(n) Question Blank 3 of 5 , pOH= 7.00 is a(n) Question Blank 4 of 5 , [H+]= 5.3 x 10^-3 is a(n) Question Blank 5 of 5arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY