
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Problem solving. Balance the substance and equat it. Kindly put your solution and answer it correctly. Refer to the picture for step by step solution if needed.
1. The chemical equation below was used the experiment conducted by students in Chem. 2 class. Determine the masses of the
Ba(NO3)2 + H2SO4 -------> BaSO4 + 2HNO3
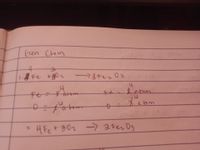
Transcribed Image Text:Gren Chem
す
abom
fes
atim
f'atom
4Fet302 3キerDs
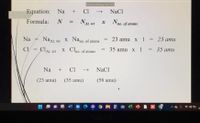
Transcribed Image Text:Remaining Meeting Time: 02:39
Equation:
Na
Cl
NaCl
Formula:
NAt. wt
Nno. of atoms
Na =
Naat, wt X Nano. of atoms
23 amu x 1:
23 ати
CI = Cl,
Clat, wt X CIno. of atoms
35 amu x I
= 35 amu
At. wt
Na
+
Cl
NaCl
(23 amu)
(35 amu)
(58 amu)
02
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Sodium carbonate is combined with calcium nitrate.a. Write the molecular, ionic equation, and net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs. b. Is there a precipitate? If so, what is the molecular formula of the precipitate and which are spectator ions? c. If 10.0 g of sodium carbonate and 10.0 g of calcium nitrate are combined, What is the limiting reactant? d. What is the maximum amount, in grams, of calcium carbonate that can be produced? e. How much excess reactant is left if all the limiting reactant is converted to products? f. If 1.0 g of calcium carbonate was collected from the reaction in part (b), what is the percent yield of the reaction?arrow_forwardA student, performing the same experiment as you, recorded the following information. The original solution was diluted by a factor of 5. Calculate the moles of acetic acid in the diluted sample. Volume of diluted vinegar sample (mL) 25.00 Molarity of NaOH 0.0900 Initial buret reading (mL) 16.50 Final buret reading (mL) 38.00 Moles of acetic acid (diluted)arrow_forwardExactly 0.7373 grams of a weak acid (HX) is added to enough water to form 50.00 mL of solution. The resulting solution requires 42.24 mL of 0.1059 M potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution to neutralize the acid. HX + KOH → KX + H₂O Please answer the following questions. A. B. C. D. What is the mass of 1 mole of the weak acid? 1 mol HX = Please provider your answer below. 0² n Determine the equilibrium concentration of HX in the solution after 23.44 mL of 0.1059 M potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution was added to the original weak acid solution. M Please provider your answer below. + 0² $ → → $ (0 grams Determine the equilibrium concentration of KX in the solution after 23.44 mL of 0.1021 M potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution was added to the original weak acid solution. M Please provider your answer below. $ Given that Ka = 3.052×10-10 for the weak acid HX, determine the pH of the solution after 23.44 mL of 0.1059 M potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution was added to the original weak acid…arrow_forward
- Solve a and b on the paper!arrow_forwardYou are analyzing a monoprotic organic acid HZ by reacting it with lithium hydroxide in a titration. You dissolve 2.27 grams of this acid in some water and titrate it with 57.94 mL of 0.379 M LiOH. What is the molar mass (in g/mole) of this monoprotic acid? Start with a balanced reaction! Report your answer to 1 decimal place and with no units. Do not use scientific notation.arrow_forward3. A log burns in a fireplace, warming the room. Is this an exothermic or an endothermic reaction? Acid-base reaction? Precipitation reaction? Redox reaction? Gas evolution reaction? Combustion reaction? Combination reaction? Dissociation reaction?arrow_forward
- 717 Sunny 2 Mo subject-RxMail-Francesca ← C app.101edu.co → STARTING AMOUNT F 2 W 4x 3 E D عالی C X F3 4 $ R F x Homepage-CHI V 19.2 14 g/mol Na % 5 T X G ADD FACTOR HOLDE Alte Chemistry XG molar mass of ox University of Deli What mass in grams of Na solid is required to completely react with 19.2 L of Ch gas at STP according to the following chemical reaction? Remember 1 mol of an ideal gas has a volume of 22.4 L at STP 2 Na(s) + Cl(g) 2 NaCl(s) x() 35.45 6.022 x 10 Dll s FS B L Na wa W A 6 39.4 68.90 g Ch Y Question 24 of 34 H N 22.99 0.857 30 1.71 & 7 1 ANDWER J □ mol Ch g/mol Ch g Na 030R PrtScn 22.4 ✰ MOD U M 19.7 8 Home K Online Payment xSign In 2 RESET 2 30.4 mol Na ( 9 O 0.0373 LCI: End L F10 ) 0 PgUp P x + Pgon12 + D 31 X I Submit 10:46 AM 7/13/202 Del Backspacearrow_forwardComplete the table below by deciding whether a precipitate forms when aqueous solutions A and B are mixed. If a precipitate will form, enter its empirical formula in the last column. solution A ammonium nitrate sodium sulfide lead(II) nitrate solution B potassium hydroxide zinc nitrate sodium carbonate Does a precipitate form when A and B are mixed? yes O yes O no O no Oyes O no empirical formula of precipitate 0 П 0 Sarrow_forwardbalance this chemical reaction ____ C6H11NO3S → ____ C3H5OS + _____ C3H6NO2arrow_forward
- Use the information and chemical equation to answer the following question: A team of chemists discovers a new chemical reaction. 2 Naci + MgF2 -> 2 NaF + MgCl2 Which type of reaction will this equation be classified as?arrow_forwardAfter titration, 25 mL of a vinegar solution was found to contain .03 moles of acetic acid. Using a density of 1.00 g/mL, what is the mass percentage of acid in the vinegar sample?arrow_forward31) You have 500 mL of a 1.25 M Pb(NO3)2 solution. How much solid sodium chloride do you need to add to react all of the lead? ? (HINT: react lead (II) nitrate with sodium chloride) а. 54.6 g b. 44.3 g с. 146 g d. 73.1 garrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY