
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The boom AB is held in equilibrium by a ball-and-socket joint A and a pulley and cord system as shown.
Determine the x, y, z components of reaction at A if F={−2200k}lb
Determine the tension in cable DEC.
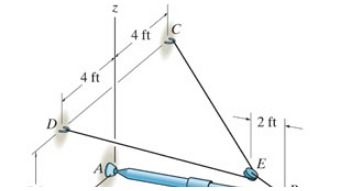
Transcribed Image Text:4 ft
4 ft
2 ft
E
A
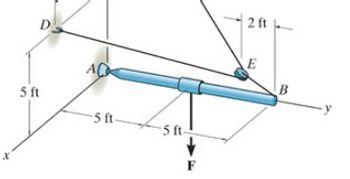
Transcribed Image Text:5 ft
-5 ft-
5 ft-
F
2 ft
E
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Member AB is supported by BC and at A by a single journal bearing with a square shaft. Determine the six equations of equilibrium for the components of the reaction at A and the tension in the cable needed to hold the rod in equilibrium (hint: use vector operations). 200 N X 400 N 1 m B 3 m Z 1.5 marrow_forward200 mm 50 Ν 250 mm 300 mm -150 mm 80 mm A 근 65 N V 80 Narrow_forward1. For the frame shown, determine the reaction at E assuming a pinned support. The tension in the cable is 150 kN. 2.25 m A B 3.75 m 20 kN 20 kN 20 kN 20 kN 1.8 m 1.8 m 1.8 m 1.8 m E F 4.5 marrow_forward
- 2. Determine the reactions at pin A and the tension at cable BC. 30 kN IB 2m- 4 m (a)arrow_forwardThe 15 kg bar AB is supported by a ball and socket joint at A, a smooth wall at B and the cable BC. The weight of the bar acts at its midpoint. Determine the tension in the cable BC and the reactions at A and B for equilibrium. 175 mm -175 mm A 300 mm. 175 mm R 250 mm. Xarrow_forwardKnowing that F = 370 N and 0 = 15°, determine the tension in the spring and reactions at A if the crank is in eqilibrium. The spring is unstretched when = 0 and remains horizontal regardless of the angle 0. F is perpendicular to arm AD. Enter the magnitude of the tension below in N to nearest whole N. (Note in this problem you can treat the spring as an unknown force and can use equilibrium to find the spring tension nor the reactions at A.) B 300 mm 150° 400 mm. In your written solution, also determine the required spring constant k for the equilibrium position described above.arrow_forward
- Determine the tension developed in cable AB, AC and AD required for equilibrium of the 450 kg cylinder.arrow_forwardDetermine the magnitude of the reaction at support A, in lb. If: P = 314 lb, h = 13 in., A = 27 in. b = 8 in.arrow_forwardQ4. Determine the support reaction on the member. The collar at A is fixed to the member and can slide vertically along the vertical shaft. 900 N 1.5 m 1.5 m 1 m 500 N- m 45arrow_forward
- 1. allows free rotation about y-axis and prevents all other displacements and rotations. The cylinder at D has a weight of 400 N. At E it is subjected to a force F = {50i + 50j – 200k} N. Determine the components of reaction at A and the tension in cable BC needed for equilibrium. Member ACD is supported by cable BC and a support at A as shown. The support at A only 0.5 m 1 m D 3 m Farrow_forwardDetermine the tensions T₁ and T₂ in the strings required to maintain equilibrium for the suspended object weighs 24N shown in the figure. B 6 T1arrow_forwardA 3-m boom is acted upon by the 4-kN force shown. Determine the tension in each cable and the reaction at the ball-and-socket joint at A.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY