
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
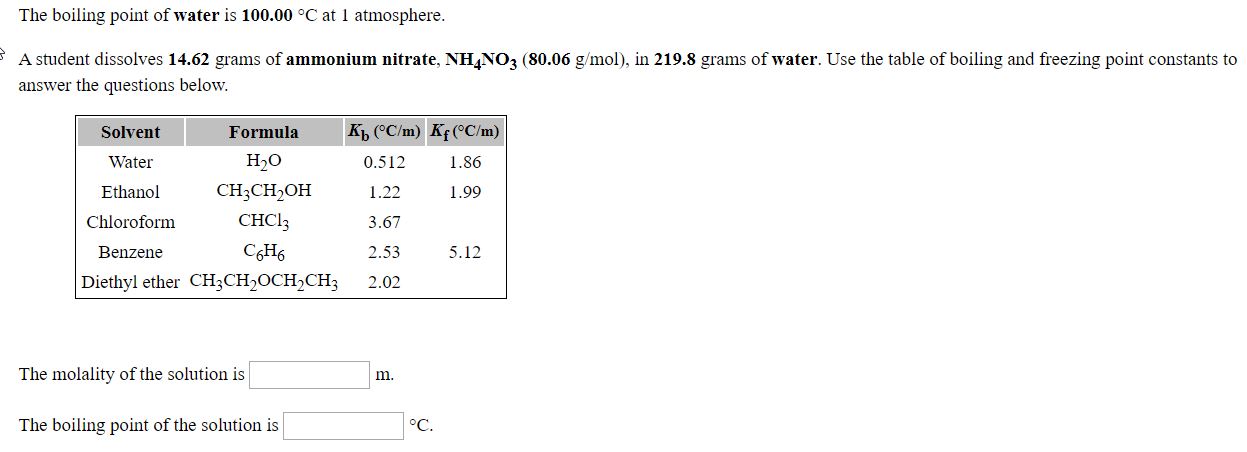
Transcribed Image Text:The boiling point of water is 100.00 °C at 1 atmosphere.
A student dissolves 14.62 grams of ammonium nitrate, NHNO3 (80.06 g/mol), in 219.8 grams of water. Use the table of boiling and freezing point constants to
answer the questions below.
Kp ("C/m) Kf(^C/m)
1.86
Solvent
Water
Ethanol
Chloroform
Formula
Н,о
0.512
1.22
CH;CH,OH
снC!
CH,
Diethyl ether CH;CH,OCH,CH3
1.99
3.67
Benzene
2.53
5.12
2.02
The molality of the solution is
m.
The boiling point of the solution is
°C.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Select the one with the highest boiling point. Select the one with the lowest freezing point. A. 1.0 m KNO3 B. 0.75 m NaCl C. 0.75 m CuCl₂ D. 2.0 m C12H22O11 (sucrose) E. pure water Determine the freezing point of a solution that contains 0.31 mol of sucrose in 175 g of water, where K₁ = 1.86°C/m. A. 3.3°C Your answer: B. 1.1°C C. 0.0°C D. -1.1°C E. -3.3°Carrow_forwardq 2req Visited 2req [Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. The boiling point of ethanol, CH3 CH₂OH, is 78.500 °C at 1 atmosphere. Kb (ethanol) = 1.22 °C/m In a laboratory experiment, students synthesized a new compound and found that when 10.17 grams of the compound were dissolved in 204.5 grams of ethanol, the solution began to boil at 78.723 °C. The compound was also found to be nonvolatile and a non-electrolyte. What is the molecular weight they determined for this compound? g/mol Submit Answer Q Graph_08-30-2....pdf NO Retry Entire Group O J A 9 more group attempts remaining I' 6 Previous Next> Show all 11:15 PM 9/12/2022arrow_forwardThe freezing point of water is 0.00°C at 1 atmosphere.A student dissolves 12.66 grams of chromium(II) acetate, Cr(CH3COO)2 (170.1 g/mol), in 281.4 grams of water. Use the table of boiling and freezing point constants to answer the questions below. Solvent Formula Kb (°C/m) Kf (°C/m) Water H2O 0.512 1.86 Ethanol CH3CH2OH 1.22 1.99 Chloroform CHCl3 3.67 Benzene C6H6 2.53 5.12 Diethyl ether CH3CH2OCH2CH3 2.02 The molality of the solution is ?The freezing point of the solution is ?arrow_forward
- Calculate the boiling point of a solution of 400 g of ethylene glycol dissolved in 400 g of water Kf= 1.86 Celsius/m and KB = 0.512 Celsius/m. Use 100 degrees Celsius as the boiling point of waterarrow_forwardWhen 20.0 grams of an unknown compound are dissolved in 500. grams of benzene, the freezing point of the resulting solution is 3.77°C. The freezing point of pure benzene is 5.444°C, and the K₁ for benzene is 5.12°C/m. What is the molar mass of the unknown compound? Hint: Round off to two significant digits. O 110 g/mol Ⓒ 120 g/mol O 130 g/mol O 140 g/mol O None of the abovearrow_forwardThe boiling point of water, H,0, is 100.00°C at 1 atmosphere. A nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte that dissolves in water is antifreeze (ethylene glycol). A student dissolves 11.07 grams of antifreeze, CH2OHCH2OH (62.10 g/mol), in 299.3 grams of water. Use the table of boiling and freezing point constants to answer the questions below. Kf Solvent Formula (°C/m) (°C/m) Water H2O 0.512 1.86 Ethanol CH;CH,OH 1.22 1.99 Chloroform CHCI3 3.67 Benzene CH6 2.53 5.12 Diethyl ether CH;CH,OCH2CH3 2.02 The molality of the solution is m. The boiling point of the solution is °C.arrow_forward
- The boiling point of water is 100.0°C at 1 atmosphere. How many grams of silver acetate (166.9 g/mol), must be dissolved in 224.0 grams of water to raise the boiling point by 0.400 °C? mpor Refer to the table for the necessary boiling or freezing point constant. Solvent Kb (°C/m) Kf(°C/m) 0.512 1.22 Chloroform CHCl3 3.67 Benzene C6H6 2.53 Diethyl ether CH3 CH₂ OCH2 CH3 2.02 g silver acetate Water Ethanol Mass = this Formula H₂O CH3CH₂OH 1.86 1.99 5.12arrow_forwardA certain liquid X has a normal boiling point of 142.00 °C and a boiling point elevation constant K = 1.03 °C kg-mol A solution is prepared by dissolving some alanine (C₂H,NO₂) in 550. g of X. This solution boils at 143.2 °C. Calculate the mass of C3H-NO, that was dissolved. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. X Sarrow_forwardAt 25.0 °C the Henry's Law constant for hydrogen sulfide (H, S) gas in water is 0.087M/atm. Calculate the mass in grams of H, S gas that can be dissolved in 1325. mL of water at 25.0 °C and a H, S partial pressure of 1.58 atm. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. x10arrow_forward
- The freezing point of ethanol, CH3CH2OH, is -117.30°C at 1 atmosphere. A nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte that dissolves in ethanol is saccharin. A student dissolves 11.77 grams of saccharin, C,H;NO3S (183.2 g/mol), in 287.1 grams of ethanol. Use the table of boiling and freezing point constants to answer the questions below. Solvent Formula Kp (°C/m) Kf (°C/m) Water H2O 0.512 1.86 Ethanol CH;CH2OH 1.22 1.99 Chloroform CHCI3 3.67 Benzene C,H6 2.53 5.12 Diethyl ether CH3CH,OCH2CH3 2.02 The molality of the solution is m. The freezing point of the solution is °C.arrow_forwardWhat is the freezing point of a solution containing 0.794 moles of a nonvolatile, non-ionic compound in 271.3 g of liquid benzene? K = 4.90°C/m for benzene, freezing point of benzene is 5.50 °C. Report your answer with the correct number of significant figures. Do not include the unit.arrow_forwardThe freezing point of ethanol, CH3CH2OH, is -117.30°C at 1 atmosphere. A nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte that dissolves in ethanol is saccharin . A student dissolves 10.10 grams of saccharin, C7H5NO3S (183.2 g/mol), in 266.8 grams of ethanol. Use the table of boiling and freezing point constants to answer the questions below. Solvent Formula Kb (°C/m) Kf (°C/m) Water H2O 0.512 1.86 Ethanol CH3CH2OH 1.22 1.99 Chloroform CHCl3 3.67 X Benzene C6H6 2.53 5.12 Diethyl ether CH3CH2OCH2CH3 2.02 X The molality of the solution is ______m.The freezing point of the solution is _____°C. FILL IN THE BLANKSarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY