
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
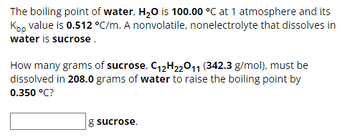
Transcribed Image Text:The boiling point of water, H₂O is 100.00 °C at 1 atmosphere and its
Kpp value is 0.512 °C/m. A nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte that dissolves in
water is sucrose.
How many grams of sucrose, C12H22O11 (342.3 g/mol), must be
dissolved in 208.0 grams of water to raise the boiling point by
0.350 °C?
g sucrose.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 13 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 15.2 g of camphor dissolved in naphthalene lower the freezing temperature of naphthalene from 80.0 °C to 75.0 °C. What is the mass of naphthalene? The molal freezing depression point constant for naphthalene is: Kf = 7.00 °C/m . Both naphthalene and camphor are non-electrolytes, and the molar mass of camphor is about 152 g/mol.arrow_forwardWhat is the freezing point (in K) of a solution made by dissolving 19.607g of CCl4 in 130.0 g of benzene? Pure benzene has a freezing point of 5.5°C and a Kf = 5.12 °C/m.arrow_forwardWhat is the freezing point of a solution that contains 475.0 g of ethylene glycol, CH2(OH)CH2(OH), which is a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte, in 5.00 kg of water? The Kf for water is 1.86 °C/m.arrow_forward
- The normal freezing point of water, H₂O is 0.00 °C and its Kip value is 1.86 °C/m. Assuming complete dissociation of the electrolyte, if 13.87 grams of barium chloride (BaCl2, 208.2 g/mol) are dissolved in 260.7 grams of water what is the freezing point of the solution? °Carrow_forwardYou are analyzing 100 g of a solution that contains 12.5 g of the ionic compound KBr (MM = 119.0 g/mol) in water. Here is some useful information: KFP of water is 1.86 °C/m; KBP for water is 0.512 °C/m. The density of the solution is 1.094 g/mL. Calculate the boiling point of this solution (bp of water is 100.0°C). Calculate the osmotic pressure (in atm) of this solution at 25°C.arrow_forwardA 83.5 g sample of a nonelectrolyte is dissolved in 206.1 g of water. The solution is determined to have a boiling point of 102.3 °C. What is the molar mass of the compound? (Kb for water is 0.510 °C/m).arrow_forward
- [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. The boiling point of ethanol, CH3 CH₂OH, is 78.500 °C at 1 atmosphere. K₁ (ethanol) = 1.22 °C/m In a laboratory experiment, students synthesized a new compound and found that when 14.95 grams of the compound were dissolved in 293.3 grams of ethanol, the solution began to boll at 78.570 °C. The compound was also found to be nonvolatile and a non-electrolyte. What is the molecular weight they determined for this compound? g/mol Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remaining Show Hint Congage Learning Cengage Technical Support Previous Next Save and Exitarrow_forwardWhen 105.g of glycine C2H5NO2 are dissolved in 1200.g of a certain mystery liquid X, the freezing point of the solution is 4.6°C lower than the freezing point of pure X. On the other hand, when 105.g of iron(III) chloride are dissolved in the same mass of X, the freezing point of the solution is 7.5°C lower than the freezing point of pure X. Calculate the van't Hoff factor for iron(III) chloride in X. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round your answer to 2 significant digits. i=arrow_forward1-A sample of pure t-butyl alcohol weighing 6.22 g was found to have a freezing point of 24.7 °C. When 0.543 g of an unknown compound X was added to the t-butyl alcohol, the mixture had a freezing point of 21.3 °C. Calculate the molar mass of compound X. (Kf = 12.8 °C/molal for t-butyl alcohol.)A sample of pure t-butyl alcohol weighing 6.22 g was found to have a freezing point of 24.7 °C. When 0.543 g of an unknown compound X was added to the t-butyl alcohol, the mixture had a freezing point of 21.3 °C. Calculate the molar mass of compound X. (Kf = 12.8 °C/molal for t-butyl alcohol.) 2-What is the rate law expression for the reaction A + B → C, based on the following dataarrow_forward
- What is the freezing point (in K) of a solution made by dissolving 19.543g of CCl4 in 130.0 g of benzene? Pure benzene has a freezing point of 5.5°C and a Kf = 5.12 °C/m.arrow_forwardCalculate the vapor pressure above a solution prepared by dissolving 2.00 g of aspirin (C9H8O4) in 50.0 g of methanol (CH3OH) at 21.2 °C. Pure methanol has a vapor pressure of 101 torr at 21.2 °C.arrow_forward11. Calculate the molality of a solution containing 398 g glucose (C,H12O6) dissolved in 2.00 L of water (density 0.997 g/mL). 12. An ethylene glycol solution contains 27.8 g of ethylene glycol (C;H,O2) in 79.2 mL of water (density 0.997 g/mL). Calculate the freezing point and boiling point of the solution.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY