
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
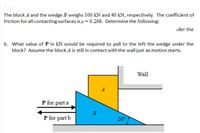
Transcribed Image Text:The block A and the wedge B weighs 100 kN and 40 kN, respectively. The coefficient of
friction for all contacting surfaces is u = 0.268. Determine the following:
ider the
b. What value of P in kN would be required to pull to the left the wedge under the
block? Assume the block A is still in contact with the wall just as motion starts.
Wall
A
P for part a
P for part b
20°7
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The beam is subjected to an internal moment of M = 140 kN.m. Determine the bending stress developed at point A,B and C.arrow_forwardA cantilever beam AB, loaded by a uniform load (see figure), is applied on a channel section. If the cross section has the dimensions indicated and the moment of inertia about the z axis (the neutral axis) is | = 3.36 in a) Find the maximum tensile stress feuaxand maximum compressive stress fyMx b) Draw the shear and moment diagram 5.0 lb/ft 0.617 in. 2.269 in. 6.0 ftarrow_forwardThe cross section of a wood beam carries a bending moment M of magnitude 20R lb.-in. acting at 100 to the horizontal. Determine(a)the angle between the neutral axis and the horizontal; and (b) the maximum bending stress acting on the cross section. Note: ( R=990)arrow_forward
- k=2 lb/ft -¨¨¨¨¨ B Two blocks A and B have a weight of 11 lb and 6 lb, respectively. They are resting on the incline for which the coefficients of static friction are μA = 0.16 and μB = 0.23. Determine the angle 0 which will cause motion of one of the blocks. What is the friction force under each of the blocks when this occurs? The spring has a stiffness of k = 2 lb/ft and is originally unstretched. Determine the smallest angle which will cause motion of one of the blocks. Determine is the friction force under the block A at this angle. Determine is the friction force under the block Bat this angle.arrow_forward1. The two homogeneous bars AB and BC are connected with a pin at B and placed between rough vertical walls. If the coefficient of static friction between each bar and the wall is 0.4, determine the largest angle 0 for which the assembly will remain at rest. 20 in. 6 lb 8 lb 20 in.arrow_forwardTake A = 150 mm^2 and E = 200 GPaarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning