
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Stresses in beams.
flexural stress.
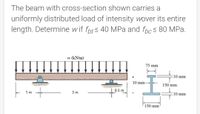
Transcribed Image Text:The beam with cross-section shown carries a
uniformly distributed load of intensity wover its entire
length. Determine w if fpts 40 MPa and fpcs 80 MPa.
w (kN/m)
75 mm
10 mm
10 mm-
150 mm
0.5 m
:10 mm
3 m
1 m
150 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- CALCULATE THE REQUIRED DIAMETER OF STEEL TIE RODS NECESSARY TO SUPPORT A BALCONY. EACH ROD, SUSPENDED FROM A ROOF TRUSS, SUPPORTS A FLOOR AREA OF 7.0m^2 THE COMBINED BALCONT FLOOR LOAD IS 10.5 kPa, INCLUDING DEAD LOAD AND LIVE LOAD. THE ALLOWABLE TENSILE STRESS IN THE STEEL TIE RODS IS 140 MPa.arrow_forwardDescribe some of the factors to be considered in the designing of the beamsarrow_forwardWhat does the existence of bracing tell you?arrow_forward
- A wood stave pipe, 48 in inside diameter, is bound by flat steel bands 4 in wide and 3/4 in thick. For an allowable stress of 16,000 psi in the steel and an internal pressure of 160 psi, determine the spacing of the bands.arrow_forwardDesigners typically specify longitudinal reinforcement on all four sides of a square column cross section for which of the following reasons? Check all that apply. Bending moments can act about two section axes, not just one O There is less chance for steel placement mistakes during construction There is additional axial strength compared to a design with longitudinal steel on only two sidesarrow_forwardwhat is the maximum bending stress ?arrow_forward
- Give the list of the various types of welded jointsarrow_forwardFor the cross section shown below, the material and sectional properties are given as follows: A) Determine the maximum steel area A_s that can lead to tension driven failure. One can use Table A.4 in the textbook to easily calculate design parameters. B) To ensure under-reinforcement, the steel area is to be decided as a value between 90% and 95% of estimated in P1(a). Determine the reinforcing bars (i.e., bar size, and the number of bars) to meet the required steel area. It is assumed that a single type of rebar is chosen (i.e., rebars of different sizes shall not be combined). C) Given the decided steel area, calculate the nominal and the design moment capacity. One cannot use the design aids.arrow_forwardDescribe the elastic strain for various types of loadings?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning