
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Microsoft Teams
Edit
View
Window
Help
Fri Feb 11 10:35:19
Search
2 AAP-Final-Exam-LPU.pdf
Close
Activity
Chat
11) An auditor's engagement letter most likely will include
A. A request for permission to contact the client's lawyer for assistance in identifying litigation, claims, and assessments.
B. A reminder that management is responsible for illegal acts committed by employees.
C. The auditor's preliminary assessment of the risk factors relating to misstatements arising from fraudulent financial
reporting.
D. Management's acknowledgment of its responsibility for such internal control as it determines is necessary to enable
the preparation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement.
Teams
12) Early appointment of the independent auditor will enable
A. A more thorough examination to be performed.
B. A proper study and evaluation of internal control to be performed.
C. Sufficient competent evidential matter to be obtained.
D. A more efficient examination to be planned.
Assignments
13) An auditor who accepts an audit engagement and does not possess the industry expertise of the business entity, should
A. Engage financial experts familiar with the nature of the business entity.
B. Obtain knowledge of matters that relate to the nature of the entity's business.
C. Refer a substantial portion of the audit to another CPA who will act as the principal auditor.
D. First inform management that an unqualified opinion cannot be issued.
Calendar
Calls
14) Engagement letters are widely used in practice for professional engagement of all types. The primary purpose of the
engagement letter is to
A. Remind management that the primary responsibility for the financial statements rests with management.
B. Satisfy the requirements of the CPA's liability insurance policy.
C. Provide a starting point for the auditor's preparation of the preliminary audit program.
D. Provide a written record of the agreement with the client as to services to be provided.
Files
15) Before accepting an audit engagement, a successor auditor should make specific inquiries of the predecessor auditor
regarding
A. Disagreements of the predecessor had with the client concerning auditing procedures and accounting principles.
B. The predecessor's evaluation of matters of continuing accounting significance.
C. The degree of cooperation the predecessor received concerning the inquiry of the client's lawyer.
D. The predecessor's assessments of inherent risk and judgments about materiality.
16) Which of the following factors would most likely cause a CPA to decide not to accept a new audit engagement?
A. The CPA's lack of understanding of the prospective client's internal auditor's computer-assisted audit techniques.
B. Management's disregard of its responsibility to maintain an adequate internal control environment.
C. The CPA's inability to determine whether related-party transactions were consummated on terms equivalent to arm's
length transaction.
D. Management's refusal to permit the CPA to perform substantive tests before the year-end.
17) Which of the following is not normally performed in the preplanning or pre-engagement phase?
A. Deciding whether to accept or reject an audit engagement
B. Inquiring from predecessor auditor
C. Preparing an engagement letter
D. Making a preliminary estimate of materiality
18) The following are considered by a CPA firm in deciding whether to accept a new client, except
A. The client's probability of achieving an unmodified opinion
B. The client's financial ability
C. The client's relations with its previous CPA firm
D. The client's standing in the business community
19) If a change in the type of engagement from higher to lower level of assurance is reasonably justified, the report based on
the revised engagement
A. Omits reference to the original engagement
B. Should always refer to any procedures that may have been performed in the original engagement.
C. Should refer to the original engagement in a separate paragraph preceding the opinion paragraph.
D. Should qualify the opinion due to a scope limitation.
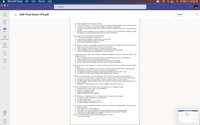
20) One of the first things that the auditor will do after accepting a new client is
Apps
A. Tour the client's facilities
Help
Transcribed Image Text:Microsoft Teams
Edit
View
Window
Help
Fri Feb 11 10:35:28
Search
2 AAP-Final-Exam-LPU.pdf
Close
Activity
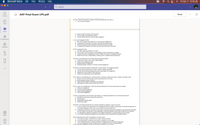
20) One of the first things that the auditor will do after accepting a new client is
A. Tour the client's facilities
Chat
Teams
B. Study the client's internal control structure
C. Communicate with predecessor auditor
D. Contact client's attorney to discover legal obligations
Assignments
21) An audit engagement letter
A. May not be prepared each period for a recurring audit engagement
B. Is prepared for the benefit of the audit, audit client and general public
C. Shall include specific audit procedures to be performed by the auditor
D. Is usually sent by auditor to the client upon the commencement of the audit
Calendar
22) The engagement letter
A. Can affect legal responsibility to the client
B. Can be used to alter the auditor's responsibilities under the standards on auditing
C. Is used only if it is an engagement, but has no effect for review or compilation services
D. Affects the CPA firm's responsibility to external users of audited financial statements
Calls
23) Which of the following is not involved during pre-planning phase?
A. Obtaining information about client's legal obligation
B. Obtaining an engagement letter
C. Selecting staff for engagement
D. Deciding whether to accept or continue an audit engagement
Files
24) Which of the following matters is least likely to be discussed in an engagement letter?
A. The fact that the auditor does not plan to detect material irregularities
B. The fact that the financial statements are the responsibility of management
C. Assistance to be provided by client personnel
D. Timing of the performance of the examination
25) To obtain an understanding of a continuing client's business in planning an audit, an auditor most likely would
A. Review prior year working papers and the permanent file for the client
B. Read specialized industry journals
C. Perform tests of details of transactions and balances
D. Reevaluate the client's internal control environment
26) It is a type of an engagement in which the financial statements for the prior period were not audited.
A. Initial audit engagement
B. Continuing audit engagement
C. Previous audit engagement
D. Future audit engagement
27) Who is responsible for the prevention and detection of material misstatements in the financial statements?
A. Management and those charged with governance
B. Internal auditor
C. Independent external auditor
D. Government auditor
28) Which of the following statements concerning materiality as regards to audit is incorrect?
A. It may be viewed as the largest amount of misstatements that the auditor could tolerate in the financial statements or
the smallest aggregate amount that could misstate the financial statements.
B. In designing an audit plan, the auditor should make a preliminary estimate of materiality for use during the examination
as some matters are important for fair presentation of financial statements while other matters are not important.
C. It is specifically provided and quantified in the Philippine Standards on Auditing (PSAS) for each industry.
D. It is a matter of professional judgment and necessarily involves quantitative and qualitative factors.
Apps
29) The following are the uses of materiality in an audit, except
A. In the planning stage, to determine the scope of audit procedures.
B. In the testing stage, to determine the amount of evidence to accumulate.
C. In the completion phase, to evaluate the effect of misstatement on the financial statements.
D. In the pre-engagement phase, to determine the capability of the client to pay audit fees.
30) The following statements concerning the planning stage are correct exoept
Help
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
The auditors include an emphasis-of-matter paragraph in an otherwise unmodified report on the entity's financial statements to emphasize that the entity being reported on had significant transactions with related parties. The inclusifis considered a qualification of the opinion.on of this separate paragraph
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
The auditors include an emphasis-of-matter paragraph in an otherwise unmodified report on the entity's financial statements to emphasize that the entity being reported on had significant transactions with related parties. The inclusifis considered a qualification of the opinion.on of this separate paragraph
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following accurately describes a characteristic of a management letter? Select all that apply. written on the auditor's letterhead O addressed to management or those charged with governance O reports internal control weaknesses O includes documentation of materiality and the audit plan O signed by managementarrow_forwardIf the auditor determines that an internal control deficiency is either a significant deficiency or a control deficiency, the auditor will issue a/an _______ on internal controls over financial reporting (ICFR) A. adverse opinion B. unmodified opinion C. unqualified opinion D. modified opinionarrow_forwardQuestion 10 When an auditor is reviewing an audit client's allowance for doubtful accounts the auditing is assessing which management assertion about the client's accounts receivables. Existance Completeness Valuation Rights and obligationsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education