
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
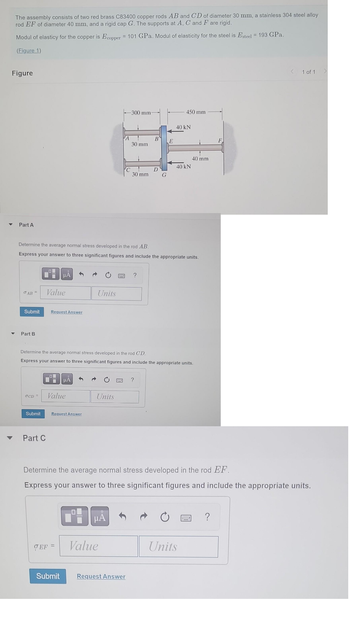
Transcribed Image Text:The assembly consists of two red brass C83400 copper rods AB and CD of diameter 30 mm, a stainless 304 steel alloy
rod EF of diameter 40 mm, and a rigid cap G. The supports at A, C and F are rigid.
Modul of elasticy for the copper is Ecopper = 101 GPa. Modul of elasticity for the steel is Esteel = 193 GPa.
(Figure 1)
Figure
▼
Part A
σAB =
Submit
Part B
Value
Submit
μÀ
Request Answer
Part C
LO
OCD = Value
Determine the average normal stress developed in the rod AB.
Express your answer to hree significant figures and include the appropriate units.
μA
Request Answer
EF =
Units
Units
A
μÃ
-300 mm-
Value
C
30 mm
Determine the average normal stress developed in the rod CD.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Submit Request Answer
30 mm
?
B
D
G
?
E
450 mm
40 kN
40 kN
40 mm
Determine the average normal stress developed in the rod EF.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Units
F
?
< 1 of 1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- #2 will upvote to anyone who will answerarrow_forwardProblem 2 14600ksi, apr For the shown structure, AB is made by C83400-red-brass (Ebr 9.8 × 10-6/ °F) and BC is made by 2014-T6-aluminum (Eal 10600ksi, a al = 12.8 × 10-6/°F). AB and BC are joined at the collar B and fixed connected at their ends. The cross sectional area of each member is 1.75 in². If there is no load in the = member when T₁ 50 °F. Now the temperature for both members are increased to T₂ = 120 °F. Determine (1) Reaction forces at fixed end C (2) The average normal stress in the member AB (3) The average normal stress in the member BC (4) Eventually, how far will the collar B be displaced? = = 3 ft 2 ftarrow_forwardUrgent, thanks fast pleasearrow_forward
- Problem 3 (20 minutes) The bars' assembly has the dimensions, diameters and materials indicated (EST 29,000 ksi; EBR = 15,000 ksi). The assembly is fixed at one end and has D in, E = 1. 10 in and F20 kip. Determine the normal force N in the bronze and the steel = d=2in = 30 d= 1 in F(kip) BRONZE ← STEEL A B ↑ c D(in) Elin 2. Draw the normal force diagram along the assembly 3. Determine the elongations ALAB (of portion AB), ALBC (of portion BC) and ALACarrow_forwardThe column above is subjected to axial loading only. Assume the following: • E= 29000 ksi G = 10000 ksi • = 986 in4 A = 60 in? • L= 20 ft • Grade 60 steel (60 ksi yield stress) • The column is fixed at the top and pinned at the bottom Which of the following is closest to the maximum normal stress the column can support (before yielding or buckling)? 167 ksi 24 ksi 42 ksi 60 ksiarrow_forwardWhat maximum load P can be applied without exceeding an allowable stress of 70 MPa for aluminum or 120 MPa for steel? Can a larger load P be carried if the length of the aluminum rod is changed. the length of the steel portion being kept the same? If so, determine this lengtharrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning