
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
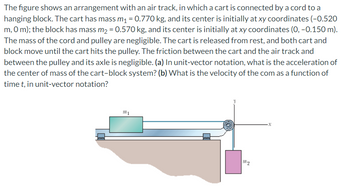
Transcribed Image Text:The figure shows an arrangement with an air track, in which a cart is connected by a cord to a
hanging block. The cart has mass m₁ = 0.770 kg, and its center is initially at xy coordinates (-0.520
m, 0 m); the block has mass m₂ = 0.570 kg, and its center is initially at xy coordinates (0, -0.150 m).
The mass of the cord and pulley are negligible. The cart is released from rest, and both cart and
block move until the cart hits the pulley. The friction between the cart and the air track and
between the pulley and its axle is negligible. (a) In unit-vector notation, what is the acceleration of
the center of mass of the cart-block system? (b) What is the velocity of the com as a function of
time t, in unit-vector notation?
CA
201
100
1₂
·x
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
The answers to this question are wrong and the solution is a bit confusing, please can you solve it again?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
The answers to this question are wrong and the solution is a bit confusing, please can you solve it again?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 76.0 kg person is riding in a car moving at 16.0 m/s when the car runs into a bridge abutment. (Assume the initial velocity is in the positive direction.) (a) Calculate the average force (in N) on the person if he is stopped by a padded dashboard that compresses an average of 1.00 cm. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) x N (b) Calculate the average force (in N) on the person if he is stopped by an air bag that compresses an average of 15.0 cm. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) X Narrow_forwardA system consists of the following masses loacted in the xy- plane: 4.0 kg at the point (0,5), 8.5 kg at the point (3,8) and 7.0 at the point (-3, -6). Find the distance from the origin to the center of mass.arrow_forwardA uniform square of mass 4 kg and sides 2 m and negligible thickness is centered at the origin. Determine thecenter of mass of this square using symmetry arguments. Suppose then that the 1 m × 1 m section in thefourth quadrant is removed. Where is the center of mass of this new object? Do this calculation by treatingthe mass of each remaining 1 m × 1 m section as residing at its center of mass and then fnding the centers ofmass of these “masses”.arrow_forward
- A uniformly loaded rectangular crate is released from rest in the position shown. Assuming that the floor is sufficiently rough to prevent slipping and that the impact at B is perfectly plastic, deter- mine the smallest value of the ratio a/b for which corner A will remain in contact with the floor. A qf b Barrow_forwardA vehicle applies brakes and skids through a distance equal to 40 m before colliding with another parked vehicle, the weight of which is 60% of the former. From fundamental principles compute the initial speed of moving vehicle, if the distance which both vehicles skid through after the collision, before stopping is 12 m. Assume average friction coefficient as 0.6. Show the various steps in the analysis and mention the assumption made in each step.arrow_forwardA 0.50-kg block slides across a table top with an initial speed of 20 cm/s and comes to rest on a distance of 70 cm. Find the average friction force that retarded its motion.arrow_forward
- ASAP likearrow_forwardthe driver of a car on a horizontal road makesan emergency stop by applying the brakes so that all four wheelslock and skid along the road.The coefficient of kinetic friction betweentires and road is 0.40.The separation between the front andrear axles is L = 4.2 m, and the center of mass of the car is locatedat distance d =1.8 m behind the front axle and distance h = 0.75 mabove the road. The car weighs 11 kN. Find the magnitude of (a)the braking acceleration of the car, (b) the normal force on eachrear wheel, (c) the normal force on each front wheel, (d) the brakingforce on each rear wheel, and (e) the braking force on eachfront wheel. (Hint: Although the car is not in translational equilibrium,it is in rotational equilibrium.)arrow_forwardA car is initially traveling at a speed of 90 km/h, suddenly brakes so that the speed becomes 36 km / h in an interval of 6 s. If style that stops the car at 3200 N, what is the mass of the car?arrow_forward
- Find the center of mass of a rod of length L whose mass density changes from one end to the other quadratically. That is, if the rod is laid out along the x-axis with one end at the origin and the of end at x = L, the density is given by p(x) = Po + (P, - PoE where Po and e, are constant values. (Use the following as necessary: L, Po, and e,.) XCM =arrow_forwardCalculate the center of mass of the upper-arm and forearm of a 75 kg athlete using the appropriate anthropometric tables, when we know the position of Marker1 is (3.5,4.5), Marker 2 is (5,3), and Marker3 is (7,4). The upper arm is defined by markers Marker1 to Marker2, whereas the forearm is defined by markers Marke2 to Marker3.arrow_forwardThe vector position of a 3.45 g particle moving in the xy plane varies in time according to i, - (3i + 35)t + 2jr? where t is in seconds and is in centimeters. At the same time, the vector position of a 5.20 g particle varies as i,- 31 - zir? - 6jt. (a) Determine the vector position (in cm) of the center of mass of the system at t = 2.90 s. x cm cm (b) Determine the linear momentum (in g cm/s) of the system at t = 2.90 s. 9. cm/s (e) Determine the velocity (in cm/s) of the center of mass at t = 2.90 s. cm/s (4) Determine the acceleration (in cm/s) of the center of mass at t = 2.90 s. cm/s? (e) Determine the net force (in µN) exerted on the two-particle system at t = 2.90 s. UN netarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON