
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
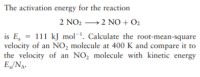
Transcribed Image Text:The activation energy for the reaction
2 NO2 →2 NO + O2
is E, = 111 kJ mol¯. Calculate the root-mean-square
velocity of an NO, molecule at 400 K and compare it to
the velocity of an NO, molecule with kinetic energy
E„/NA.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 1) The rate constant for the gas-phase reaction H2(g) + I2(g) → 2 HI(g) has the value 4.45 x 10-5 mol-1 dm³ s-1. What is the equivalent rate constant in units of molecule-1 cm³ s- 1? 2) The kinetics of the hydrolysis of methyl methanoate, CH3COOCH3, in aqueous solution were investigated by measuring the concentration of the ester after different time intervals. The reaction was found to be first order in the concentration of the ester. Use the data below to determine the rate constant for the reaction (must provide best fit graph). 3600 time, t/s 1800 5400 7200 9000 concentration, c/ (mol dm-3) 0.300 0.191 0.135 0.081 0.055 0.035arrow_forwardThe gas phase decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide at 335 K 2 N205 →4 NO2+02 has the following relationship between rate and concentration, where the bracket around the formula indicates concentration and k is a constant called the rate constant. Rate = k[N2O5l %3D If the value of k is 7.38×10~$ s', what is the rate of the reaction when [N2O5] = 0.180 M? Ms-arrow_forwardThe reaction 2 H2O2(aq) ➝ 2 H2O(l) + O2(g) is first order in H2O2 and under certain conditions has a rate constant of k = 0.00752 s-1 at 20.0ºC. A reaction vessel initially contains 150.0 mL of 30.0 % H2O2 by mass solution. The density of the solution is 1.11 g/mL. The gaseous oxygen is collected over water at 20.0ºC as it forms. What volume of O2 forms in 85.0 seconds at a barometric pressure of 742.5 mmHg? The vapor pressure of water at this temperature is 17.5 mmHg.arrow_forward
- The specific rate constant for the first-order decomposition of -1 N₂O5 (9) to NO2 (g) and O₂ (g) is 7.48 × 10-³ s¯ at a given temperature. Find the length of time required for the total pressure in a system containing N₂O5 at an initial pressure of 0.110 atm to rise to 0.150 atm . Express your answer using two significant figures. VE ΑΣΦ t = Submit Part B t = Submit Request Answer Find the length of time required for the total pressure in a system containing N₂O5 at an initial pressure of 0.110 atm to rise to 0.220 atm . Express your answer using two significant figures. ΨΕ ΑΣΦ Part C Request Answer ? Find the total pressure after 120 s of reaction. S Sarrow_forwardThe Arrhenius parameters for the gas-phase decomposit ion of cyclobutane, C4H8(g)→ 2 C2H4(g). are log(A/s-1) = 15.6 and Ea = 261 kJ mol- 1. What is the ha lf- life of cyclobutane at (a) 20 °C, (b) 500 °C?arrow_forwardIn a study of the gas phase decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide at 335 K N2O5(g)2 NO,(g) + ½ O2(g) the concentration of N2O5 was followed as a function of time. It was found that a graph of In[N,O3] versus time in seconds gave a straight line with a slope of -7.38×10-3 s and a y-intercept of -3.13. Based on this plot, the reaction is | order in N2O5 and the half life for the reaction i | seconds.arrow_forward
- complete all stepsarrow_forwardA gas phase reaction has a rate coefficient of 1.3·104 L mol–1s–1 at 300 K and its activation energy is 8.3 kJ mol–1. Indicate the order of the reaction.arrow_forward4. For the reaction: N,0,(g) = 2NO,(g) Assuming initial mass m of N,0,(g) and constant temperature (T) and Derive the relation between: (1) (i) The ratio of initial volume V, and average molar mass at equilib initial molar mass M, final volume V, (ii) Tho don 0000iarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY