
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
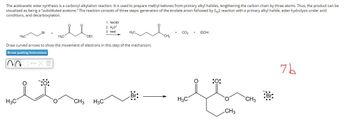
Transcribed Image Text:The acetoacetic ester synthesis is a carbonyl alkylation reaction. It is used to prepare methyl ketones from primary alkyl halides, lengthening the carbon chain by three atoms. Thus, the product can be
visualized as being a "substituted acetone." The reaction consists of three steps: generation of the enolate anion followed by SN2 reaction with a primary alkyl halide, ester hydrolysis under acid
conditions, and decarboxylation.
м
Br
H3C
H3C
OEt
1. NaOEt
2. H₂O*
3. heat
H₂C.
Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism.
CO₂
EtOH
CH3
Arrow-pushing Instructions
H3C
1:0:
:0:
:Br:
Br:
H₂C
CH3
CH3
H3C
CH3
7b
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 1 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Predict the products, propose mechanisms for the reactions of carboxylic acidderivatives with reducing agents, alcohols, amines, and organometallic reagentssuch as Grignard, organolithium, and organocuprate reagentsarrow_forwardStarting with cyclohexanone and ethanol as the only organic reagents, use any inorganic reagents to propose a synthesis for the target molecule.arrow_forwardGive steucture of organic and inorganic products of the following sn2 reaction, and identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group.arrow_forward
- Draw the structures of all possible products formed from the following reaction. Specify the type of substitution or elimination pathway. Demonstrate the sterrochemical outcomes of the reaction by drawing your products in wedge dash form when necessary.arrow_forwardGive the major organic product for each of the reactionsarrow_forward47) Provide the structure of the major organic product which results in the following reaction. Br KI Br CH3arrow_forward
- how to synthesize 2-phenylclohexanone from cyclohexanone?arrow_forwardDraw the structure(s) of the major organic product(s) of the following reaction. aqueous H₂SO + KCNarrow_forward1. NaOEt CO₂Et 2. H3O+ 3. heat Br H3C CO₂H CO2 H3C CO₂Et The malonic ester synthesis is a carbonyl alkylation reaction. It is used to prepare carboxylic acids from primary alkyl halides, lengthening the carbon chain by two atoms. Thus, the product can be visualized as being a "substituted acetic acid." The reaction consists of three steps: generation of the enolate anion followed by SN2 reaction with a primary alkyl halide, ester hydrolysis under acid conditions, and decarboxylation. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions 22 CX EtO₂C EtO₂C HOCH2CH3 HOCH2CH3 EtO₂C EtO₂Carrow_forward
- How would you perform an experiment to produce cyclohexanol from cyclohexene? Describe in detail the reagents and glassware you would use including approximate amounts and concentrations of reagents. What steps would be needed to purify the cyclohexanol from the other reagents used in the reaction?arrow_forwardAlkenes can be converted into alcohols by acid-catalyze addition of water. Predict the major alcohol product from this alkene below.arrow_forwardAcetal derivatives of aldehydes and ketones are prepared by an acid-catalyzed dehydration reaction with alcohols or diols. Using more pictures than words, draw a reaction and a mechanism that shows the formation of acetal.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY