
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:ne
m Course: 2021SP Prin of Financial Accounting (ACC-120-1)
C CengageNOWv2 | Online teaching and learning resource fn
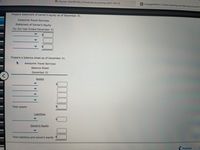
Prepare statement of owner's equity as of December 31.
Awesome Travel Services
Statement of Owner's Equity
For the Year Ended December 31
Prepare a balance sheet as of December 31.
Awesome Travel Services
Balance Sheet
December 31
Assets
$
Total assets
Liabilities
Owner's Equity
Total liabilities and owner's equity
Previous
%24
%24
%24
Transcribed Image Text:v2.cengagenow.com
Students Home
Tn Course: 2021SP Prin of Financial Accounting (ACC-120-11)
C CengageNOWv2 | Online teaching and learning resource from Cengage Lear
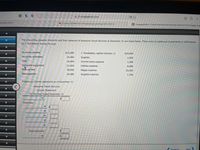
The accounting equation elements and their balances of Awesome Travel Services at December 31 are listed below. There were no additional investments or withdrawals
by J. Trendsetter during the year.
Accounts payable
$12,000
J. Trendsetter, capital (January 1)
$10,000
Accounts receivable
14,000
Supplies
1,000
Cash
18,000
Income taxes expense
1,300
Computer equipment
21,000
Utilities expense
8,000
Fees earned
78,000
Wages expense
25,000
Rent expense
10,000
Supplies expense
1,700
Prepare an income statement as of December 31.
Awesome Travel Services
Income Statement
For the Year Ended December 31
$
Expenses:
Total expenses
Previous
Next
%24
%24
%24
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help me fill out this table. Thank you so much.arrow_forward6 Mario Company's Accounts Receivable balance atDecember 31 was $300,000 and there was a credit balance of $1,400 in the Alowance for Doubtful Accounts, The year's sales were $1,800,000. Mario estimates credit losses for the year at 1.5% of sales. After the appropriate adjusting entry is made for credit losses, what is the net amount of accounts receivable included in the current assets at year- end? A) $300,000 B) $271,600 C) $325,400 D) $277,400arrow_forwardOn the basis of the following data related to assets due within one year for simmons Co. prepared partial balance sheet in good from at december 31, show total current asset Cash 96,000 Notes receivable 50,000 Accounts receivable 275,000 Allowance for Doubtfull Account 40,000 Interest Receivable 1,000arrow_forward
- On December 31, 20X1, the company reported a debit balance of $200,000 in accounts receivable and a credit balance of $5,000 in the allowance for expected credit losses. December 31 is the company’s reporting date. During 20X2, the company had the following transactions: a. The company made a credit sale of $300,000. b. The company collected accounts receivable for 350,000. c. The company wrote off the uncollectible accounts for $12,000. d. The company collected the receivable of $4,000 that had been written off previously. Required Note: Show calculation: (1) Prepare journal entries to record the above four transactions. (2) Assume that 2% of the company’s accounts receivable cannot be collected, prepare the adjusting journal entry at the end of 20X2.arrow_forwardThe accounts of Long Company provided the following 20X5 information at 31 December 20X5 (end of the annual period): Accounts receivable balance, 1 January 20X5 $51,000 Allowance for doubtful accounts balance, 1 January 20X5 3,000 Uncollectible account to be written off during 20X5 (ex-customer Slo) 1,000 Cash collected on accounts receivable during 20X5 170,000 Estimates for bad debt losses: Based on ending balance of accounts receivable, 8%. Based on aging schedule (excludes Slo’s account): Age Accounts Receivable Probability of Noncollection Less than 30 days $28,000 2% 31–90 days 7,000 10 91–120 days 3,000 30 More than 120 days 2,000 60 Required: Give the entry to write off customer Slo’s long-overdue account. Give all entries related to accounts receivable and the allowance account for the following two cases: Case A—Bad debt expense is based on the ending balance of accounts receivable Case B—Bad debt expense is based on aging Show how the results of applying each case above…arrow_forward1. The following account balances were extracted from the accounting records of Macy Corporation at the end of the year:Accounts Receivable $1,100,000Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts (Credit) $37,000Uncollectible-Account Expense $63,000What is the net realizable value of the accounts receivable? Select one:A. $1,163,000B. $1,137,000C. $1,100,000D. $1,063,000 Please show all steps.arrow_forward
- The year-end financial statements of Prize Inc. include the accounts receivable footnote:Total accounts and other receivables at December 31 consisted of the following: (in millions) Year 2 Year 1 Total accounts and other receivables $444.4 $476.6 Allowance for doubtful accounts (6.0) (8.4) Total accounts and other receivables, net $438.4 $468.2 The balance sheet reports total assets of $2,984.1 million at December 31, Year 2.The common-size amount for gross accounts and other receivables are: Select one: a. $444.4 million b. None of these are correct. c. 14.7% d. 14.9% e. $438.4 millionarrow_forwardThe balance sheet of RS Corp. as at December 31, 1979 contained the following current assets: Cash 96, 578 Accounts receivable 452,800 Inventories 376,300 925,678 An examination of the accounts disclosed that the accounts receivable consisted of the following items: Trade customers’ accounts 357,742 Due from employees – current 43,658 Equity in 50,000 of uncollected accounts receivable assigned under guaranty 16,000 Selling price of merchandise on consignment at 140% of cost and not sold 50,400 Allowance for doubtful accounts…arrow_forwardIn the first year of operations, Ralph's Repair Service recognized $482,000 of service revenue earned on account. The ending accounts receivable balance was $88,900. Ralph estimates that 2% of sales on account will not be collected. During the year, Ralph wrote off a $200 receivable that was determined to be uncollectible. Assume there were no other transactions affecting accounts receivable. Required: a. What amount of cash was collected in Year 1? b. What amount of uncollectible accounts expense was recognized In Year 1? c. What will be Ralph's net realizable value of receivables on the December 31, Year 1 balance sheet? a. Cash collected b. Uncollectible accounts expense c. Net realizable value of receivablesarrow_forward
- Sherwood, Inc., had the following current assets and current liabilities at the end of two recent years: Year 2(in millions) Year 1(in millions) Cash and cash equivalents $4,165 $4,528 Short-term investments, at cost 2,958 8,408 Accounts and notes receivable, net 9,404 8,624 Inventories 1,771 787 Prepaid expenses and other current assets 590 291 Short-term obligations (liabilities) 315 3,342 Accounts payable and other current liabilities 7,453 6,813 a. Determine the (1) current ratio and (2) quick ratio for both years. Round to one decimal place. Year 2 Year 1 Current ratio fill in the blank 1 fill in the blank 2 Quick ratio fill in the blank 3 fill in the blank 4arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardPlease SHOw your workarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education