
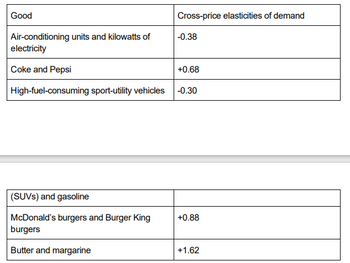
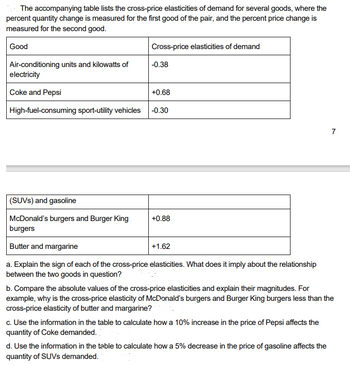
The accompanying table lists the cross-
percent quantity change is measured for the first good of the pair, and the percent price change is
measured for the second good.
( please see image)
a. Explain the sign of each of the cross-price elasticities. What does it imply about the relationship
between the two goods in question?
b. Compare the absolute values of the cross-price elasticities and explain their magnitudes. For
example, why is the cross-price elasticity of McDonald’s burgers and Burger King burgers less than the
cross-price elasticity of butter and margarine?
c. Use the information in the table to calculate how a 10% increase in the price of Pepsi affects the
quantity of Coke demanded.
d. Use the information in the table to calculate how a 5% decrease in the price of gasoline affects the
quantity of SUVs demanded.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

- 1. If the cross-price elasticity of Coke/Pepsi is +0.63, what is relationship between the price of Coke and the demand for Pepsi?arrow_forwardQ11arrow_forwardExplain in your own words what information the income elasticity of demand provides. If a good is an inferior good, what will the sign of the income elasticity of demand be? Explain.arrow_forward
- question # 2 and 14arrow_forwardSuppose Left Shoes and Right Shoes were sold separately. a. Do you think the cross-price elasticity of Left Shoes and Right Shoes would be positive or negative?b. Given the answer to (a) how would you describe the relationship between these two goods? c. The person who makes Right Shoes increases the price of Right Shoes. How does this effect demand for Left Shoes? d. Use a graph to illustrate your answer to (c).arrow_forwardData from the Bureau of Labor Statistics shows that U.S. income increased by 10% while consumer data shows that the quantity demanded of organic lemonade drinks changed from 80 to 85. Compute the income elasticity for organic lemonade drinks, is organic lemonade a normal or an inferior good?arrow_forward
- To calculate an elasticity coefficient of demand, we need to Divide the percentage change in the price by the percentage change in the quantity demanded Multiply the percentage change in the quantity demanded by the percentage change in the price Know the slope of the demand curve Multiply the percentage change in the price by the percentage change in the quantity demandedarrow_forwardThe price of Samsung mobile phones rises from £175 to £125. This leads to an increase in the quantity demanded of Nokia mobile phones from 8375 per week to 8750. What is the cross price elasticity of demand for the mobile phones? What does this this suggest about the relationship between the two products?arrow_forwardSuppose that demand schedule for discs is represented in the table below. PRICE ($) 8 10 QUANTITY DEMANDED (INCOME $10,000) 40 32 QUANTITY DEMANDED (INCOME $12,000) 50 46 If your income is $12,000, use the midpoint method to calculate your price elasticity of demand as the price of compact discs increases from $8 to $10. Select one: O a. The price elasticity of demand for discs is equal to -1.25 and demand is elastic. b. The price elasticity of demand for discs is equal to -1 and demand is inelastic. c. The price elasticity of demand for discs is equal to -0.375 and demand is inelastic. Od. The price elasticity of demand for discs is equal to -1 and demand is unit elastic.arrow_forward
- When the price of A increase by 30%, the consumption of the good decreased by 10%, what is the price elastic of demand? Will the total revenue of selling the good increase or decrease when the price of good A increase? When the price of A increase by 10%, the consumption of the good B increases by 20%, what is the cross-price elasticity of demand of B with the change of price of A?arrow_forward4-6 Suppose that the price of croissants rises from $2 to $3 per unit. Use the mid-point approach to get the elasticity. answer the following The quantity of orange juice purchased falls from 10 million bottles to 5 million bottles. What is the cross-price elasticity of demand between croissants and orange juice? Are they complements or substitutes? The quantity of jelly purchased increases from 10 million jars to 20 million jars. What is What is the cross-price elasticity of demand between croissants and jelly? Are they complements or substitutes?arrow_forward2. The accompanying table lists the cross - price elasticities of demand for several goods, where the percent quantity change is measured for the first good of the pair, and the percent price change is measured for the second good. a. Explain the sign of each of the cross - price elasticities. What does it imply about the relationship between the two goods in question? b. Compare the absolute values of the cross - price elasticities and explain their magnitudes. For example, why is the cross - price elasticity of McDonald's burgers and Burger King burgers less than the cross - price elasticity of butter and margarine? Use the information in the table to calculate how a 5% increase in the price of Pepsi affects the quantity of Coke demanded. d. Use the information in the table to calculate how a 10% decrease in the price of gasoline affects the quantity of SUVS demanded. Cross-price Good elasticities of demand Air - conditioning units and kilowatts of electricity Coke and Pepsi High -…arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





