
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
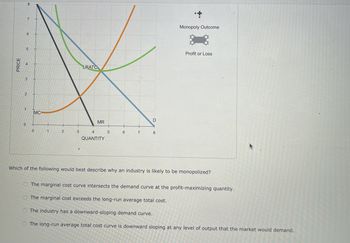
Transcribed Image Text:PRICE
6
5
3
2
1
0
0
MC
1
2
3
LRATO
MR
4
QUANTITY
5
6
7
D
8
Monopoly Outcome
Profit or Loss
Which of the following would best describe why an industry is likely to be monopolized?
The marginal cost curve intersects the demand curve at the profit-maximizing quantity.
The marginal cost exceeds the long-run average total cost.
The industry has a downward-sloping demand curve.
O The long-run average total cost curve is downward sloping at any level of output that the market would demand.
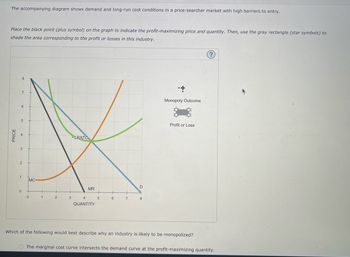
Transcribed Image Text:The accompanying diagram shows demand and long-run cost conditions in a price-searcher market with high barriers to entry.
Place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity. Then, use the gray rectangle (star symbols) to
shade the area corresponding to the profit or losses in this industry.
PRICE
6
7
5
2
1
0
MC
0
1
2
3
LRATO
MR
QUANTITY
5
6
7
D
8
Monopoly Outcome
Profit or Loss
Which of the following would best describe why an industry is likely to be monopolized?
O The marginal cost curve intersects the demand curve at the profit-maximizing quantity.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5. Imagine a monopolist could charge a different price to every customer based on how much he or she was willing to pay. How would this affect monopoly profits?arrow_forwardNote:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardReview the graph at right for a monopoly market (enter all of your responses as whole numbers). Price 100- How much is the consumer surplus? S 90- MC How much is the producer surplus? s 80- 70- How much is the deadweight loss? S 60 80- Monopoly total surplus is $ 50- Monopoly total surplus is V competitive total surplus. 40- 30- 20- 10- MR D 10 30 40 50 60 70 90 100 Quantityarrow_forward
- N6arrow_forward8. Natural monopoly analysis The following graph gives the demand (D) curve for 5G LTE services in the fictional town of Streamship Springs. The graph also shows the marginal revenue (MR) curve, the marginal cost (MC) curve, and the average total cost (ATC) curve for the local 5G LTE company, a natural monopolist. On the following graph, use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity for this natural monopolist. PRICE (Dollars per gigabyte of data) 20 18 16 14 12 10 80 6 4 2 0 0 1 MR 2 3 4 5 6 7 QUANTITY (Gigabytes of data) 8 ATC MC 9 10 D Monopoly Outcome Which of the following statements are true about this natural monopoly? Check all that apply.arrow_forwardQuestion 5 The following figure describes the market demand curve of a monopoly market: 10 Price, cost 9 8 7 6 3 2 1 a. b. C. d. 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 D a). 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 quantity Draw the marginal revenue (MR) curve for the monopoly given the above market demand curve. If the monopoly firm can produce any output level with the extra cost $3 per unit, how would the marginal cost (MC) curve be? List the mathematical equation and draw the MC curve on the same figure of question The fixed cost for the monopoly company is $25. Find the optimal output level and the related profit/loss for it. There are two proposals concerning the market efficiency: Plan A: regulate the market price at $4. Plan B: allow and help the monopoly enforce the perfect price discrimination. If you represent consumers to vote for one plan, which one would you choose? Explain with proper calculation (Hint: consumers only care about their welfare).arrow_forward
- 8arrow_forwardP $9 $7 55 B 300 rounds 740 rounds. 900 rounds MC ATC 1.200 rounds MRWD DWD $10 $9 0 100 200 350 Q 0 100 120 200 Q The graphs represent the demand for use of a local golf course for which there is no significant competition. It has a local monopoly.) P denotes the price of a round of goif and Q is the quantity of rounds sold each day. If the left graph represents the demand during weekdays and the right graph the weekend demand then over the course of a full seven-day week, this price discriminating profit-maximizing golf course should sel a total of $4 MRWE MC ATC Pwearrow_forwardUse the following information to answer questions 1 through 4: The table below shows data for the production of Apples for an individual firm operating as a monopoly. 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Quantity of Apples Price Total Costs 600 3000 550 3750 500 4750 450 6000 400 8500 350 12500 300 20000 250 32000 200 43500 Monopoly Problem Set¹ 1. Given this data, complete the table: Profit Quantity of Apple Price 0 10 20 30 40 50 Total TC Revenue (TR) Marginal Revenue (MR) Marginal Costs (MC) 2. At what quantity are marginal revenues equal to marginal costs?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education