
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
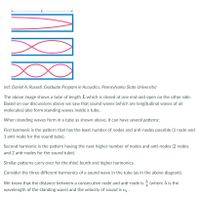
Transcribed Image Text:(ref: Daniel A. Russell, Graduate Program in Acoustics, Pennsylvania State University)
The above image shows a tube of length L which is closed at one end and open on the other side.
Based on our discussions above we saw that sound waves (which are longitudinal waves of air
molecules) also form standing waves inside a tube.
When standing waves form in a tube as shown above, it can have several patterns:
First harmonic is the pattern that has the least number of nodes and anti-nodes possible (1 node and
1 anti-node for the sound tube).
Second harmonic is the pattern having the next higher number of nodes and anti-nodes (2 nodes
and 2 anti-nodes for the sound tube).
Similar patterns carry over for the third, fourth and higher harmonics.
Consider the three different harmonics of a sound wave in the tube (as in the above diagram).
We know that the distance between a consecutive node and anti-node is (where A is the
wavelength of the standing wave) and the velocity of sound is v, .

Transcribed Image Text:Which of the following gives the wavelength of the third harmonic of the sound wave as in the
above diagram ?
O A = -4L
4L
4L
O A =
%3D
X = 4L
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The acoustical system shown in the figure below is driven by a speaker emitting sound of frequency 859 Hz. (Use v = 343 m/s.) Sliding section Speaker Receiver Ⓡ (a) If constructive interference occurs at a particular instant, by what minimum amount should the path length in the upper U-shaped tube be increased so that destructive interference occurs instead? m (b) What minimum increase in the original length of the upper tube will again result in constructive interference? marrow_forwardSummarize waves as they pass through slits. demonstrate “Put up a barrier to see how the waves move through one or two slits. What sort of pattern do the slits create? How can you change this pattern?”arrow_forwardDescribe why Young used a single slit and then a double slit in his double-slit experiment.arrow_forward
- The diagram below shows the wave crests for two sources that are totally in phase. For each of the labeled points, determine whether the light intensity (not the wave amplitude) is a minimum or a maximum. B S, Maximum Minimum Neither Submit Answer Tries 0/100arrow_forwardTwo radio antennas separated by d = 302 m, as shown in the figure below, simultaneously broadcast identical signals at the same wavelength. A car travels due north along a straight line at position x = 1,040 m from the center point between the antennas, and its radio receives the signals. Hint: Do not use the small-angle approximation in this problem. (a) If the car is at the position of the second maximum after that at point O when it has traveled a distance of y = 400 m northward, what is the wavelength of the signals? m (b) How much farther must the car travel from this position to encounter the next minimum in reception?arrow_forwardInteity rty (500nm Question: Explain how your screenshots show the two different types of wave interference - constructive and destructive. Please explain your answer in at least two complete sentences.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON