
Concept explainers
This is the equations I learnt so far and can apply to this
W = FS cos θ
W = FS
Kinetic Energy (KE = ½ mv2) & PE = mgh
Eff= Wo/W& Eff=FoD0/ FiDi & Eff=AMA/IMA
Momentum(P = mv)
m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
Impulse(J = Ft
= m Δv)
Friction (F = μN)
Power=Work/Time= Force x Displacement /Time
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 20 images

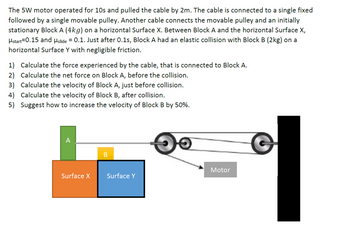
Can tutor be more clearly on why it need to times 1.5 and how to make use the formula to make it increase the velocity of Block B by 50%
For questions 4)r Calculate the velocity of Block B, after collision.
can tutor use m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2 and u1 – u2 = v2 – v1 to do ? as it is a elastic collision and my lecture need us to use this two equation for elastic collision to solve the velocity
can u explain questions Q3 more clearly and am I able to apply the momentum formula ?
I do not understand the questiona 1 Calculation of force experience d by cable connected to block A, why using equation P=F/t x s instead of using work done formula and what is Fa=4F
Why i cannot just do like this:
Work = Power x Time = 5W x 10s = 50 Joules
Force = 50 Joules / 2 meters = 25 Newtons
and can tutor explain other questions like what is the equation means
can tutor continue the next two questions also
Can tutor be more clearly on why it need to times 1.5 and how to make use the formula to make it increase the velocity of Block B by 50%
For questions 4)r Calculate the velocity of Block B, after collision.
can tutor use m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2 and u1 – u2 = v2 – v1 to do ? as it is a elastic collision and my lecture need us to use this two equation for elastic collision to solve the velocity
can u explain questions Q3 more clearly and am I able to apply the momentum formula ?
I do not understand the questiona 1 Calculation of force experience d by cable connected to block A, why using equation P=F/t x s instead of using work done formula and what is Fa=4F
Why i cannot just do like this:
Work = Power x Time = 5W x 10s = 50 Joules
Force = 50 Joules / 2 meters = 25 Newtons
and can tutor explain other questions like what is the equation means
can tutor continue the next two questions also
- A scale model of a pump has been tested and the following results obtained. Impeller diameter (D) 110mm Power input (P) 2.5kW Speed (N) 1500 r.p.m. Flow (Q) 14.5 litres/sec Head (H) 17m Efficiency (E) 60% You are to determine the speed and size of a geometrically similar pump which would deliver a flow rate of 25 litres/sec against a 22m resistance head. Determine the power input required by this pump.arrow_forwardQ4/A- The mass of the filter is 25.3046 gm. after 20 min the filter mass will be 25.4112 gm. with volumetric flow is 5.2 m 3/hr. What is the concentration of pollutant after one dayarrow_forwardI need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





