
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
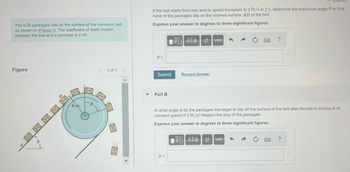
Transcribed Image Text:The 5-lb packages ride on the surface of the conveyor belt
as shown in (Figure 1). The coefficient of static friction
between the belt and a package is 0.45.
Figure
0.
6 in.
6
<
1 of 1 >
If the belt starts from rest and its speed increases to 2 ft/s in 2 s, determine the maximum angle so that
none of the packages slip on the inclined surface AB of the belt.
Express your answer in degrees to three significant figures.
0 =
Submit
Part B
Avec
b =
Request Answer
At what angle do the packages first begin to slip off the surface of the belt after the belt is moving at its
constant speed of 2 ft/s? Neglect the size of the packages.
Express your answer in degrees to three significant figures.
IVE| ΑΣΦ | 41
?
vec
?
O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 130-lb crate is being transported by a 175-lb hand- truck cart along the frictionless floor. The coefficients of friction between the cart and the box are μ = 0.20 and Mk = 0.15. If a force P = 45 lb is applied as shown, P determine the smallest ratio d/b for which the box will tip before it slides. Neglect the mass of the wheels of the cart. Show the complete and clear solutions including the necessary diagrams (i.e., FBD and the KD diagrams).arrow_forwardIn an amusement park ride, riders stand against the vertical wall of a spinning cylinder. The floor falls away and the riders are held up by friction. If the radius of the cylinder is R, find the minimum number of revolutions per time necessary if the coefficient of friction between a rider and the wall is given.arrow_forwardA carnival ride has people stand inside a vertical cylinder with their backs to the wall. The cylinder starts spinning and the riders find that they are “stuck” to the wall and don’t slide down, even if the floor is removed. The ride has a radius of r. The person has a mass of m and is moving with a constant speed of v. The coefficient of static friction between the person and the wall is μs , and kinetic friction μk. The person is only touching the wall, not touching the floor. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the person? In what direction does it point? The speed is constant. Why is the acceleration not zero? Briefly explain. No equations!arrow_forward
- The uniform 52-kg slender bar is initially at rest on a smooth horizontal plane when the forces are applied. If P₁ = 20 N and P₂ = 86 N, they are constant and are always perpendicular to the slender bar, determine angle (in degree) when time t = 0.40 s has passed. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. 0.75 m P₁ Your Answer: Answer 1.75 m 0.5 m P₂arrow_forwardThe block has a mass of 140 kg and rests on a surface for which the coefficients of static and kinetic friction are Hs = 0.5 and uj. = 0.4, respectively. (Figure 1) Part A If a force F = (60t2 ) N, where t is in seconds, is applied to the cable, determine the power developed by the force when t = 5 s. Hint: First determine the time needed for the force to cause motion. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. µA ? P = Value Units Figure 1 of 1 Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forwardUnder the man's pushing force P = 37.3 lb, the uniform cabinet is sliding on the ground with a constant acceleration of a. If the uniform cabinet has weight of 150 lb, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the cabinet and the ground is uk = 0.14, determine the normal force reaction under leg A. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point and proper unit. Take g = 32.2 ft/s2. -1 ft→+–1 ft-→| P 4 ft 3.5 ft A В Your Answer: Answer unitsarrow_forward
- Situation 5: Suppose the coefficient of kinetic friction between me and the plane as shown in figure is µ = 0.2 and that m = 20 kg and m² = 20 kg 53. What is the acceleration of Block A 0.605 -0.605 0.303 -0.303 60° 54. What is the tension on the chord? 80.31 N 72.12 N 78.17 N 66.71 N 1.1 m/s 52. What is mass of block B in order to move 1m up in an inclined when the block initially at rest 18.83 kg 20.41 kg 15.61 kg 25.12 kg 30° 55. What is the time required for block B to reach the top assuming it is initially 2.5 m away. 4.06 S 1.07 s 2.87 s 3.24 sarrow_forwardThe 2-kg spool S fits loosely on the inclined rod for which the coefficient of static friction is μ = 0.28. (a) If the spool is located 0.25 m from A, determine the maximum constant speed the spool can have so that it does not slip up the rod. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardThe 250-lb pipe is being towed behind a truck, as shown in the figure. If θ = 25° and the coefficient of friction of the pipe with the ground is μk = 0.25, determine: a) the tension in the cable b) the acceleration of the truckarrow_forward
- If the uniform cabinet has weight of 200 lb, and the coefficient of static friction between the cabinet and the ground is g = 0.14, determine the minimum force P that can make the cabinet slide. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 1 place after the decimal point and proper unit. Take g = 32.2 ft/s². Your Answer: Answer P 4 ft units A -1 ft-1 ft- 3.5 ft Barrow_forwardI am not entirly sure what system this problem is decribing. what do the fbd's for this look like?arrow_forwardThe 60-kg crate shown in (Figure 1) starts from rest and attains a speed of 6 m/s when it has traveled a distance of 15 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the ground is μ = 0.3. Figure 1 of 1 (> ▲ Part A Determine the force P acting on the crate. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. P= DH μA 6 Submit Value Provide Feedback Request Answer Units ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY