
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
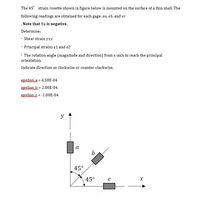
Transcribed Image Text:The 45° strain rosette shown in figure below is mounted on the surface of a thin shell. The
following readings are obtained for each gage: ea, eb, and ec
.Note that Be is negative.
Determine:
• Shear strain yxy
• Principal strains e1 and e2
· The rotation angle (magnitude and direction) from x-axis to reach the principal
orientation.
Indicate direction as clockwise or counter-clockwise.
epsilon a = 4.50E-04
epsilon k= 2.00E-04
epsilons = -1.00E-04
%3D
y
а
b
45°
45°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two [0°, 45°, 90°] strain gauge rosettes are placed along the neutral axis of a 4-point bent beam as shown in the figure below. What will the strain reading in each of the 6 gauges be? P L/3 L/3 -45° 45 L/4 L/2 L NA harrow_forwardThree readings are obtained from an equiangular strain gage rosette mounted on a free and unloaded surface of a part. Determine the magnitude of the principal strains and their orientation with respect to the 0° gage. Check the results with a Mohr circle.Assume The three known strains are all linear strainsarrow_forwardThe rigid beam is supported by a pin at A and wires BD and CE. Figure 3 m 2m 1 of 1 4 m ▾ Part A If the load P on the beam causes the end C to be displaced 8 mm downward, determine the normal strain developed in wire CE. (Figure 1) ECE = Submit ▾ Part B EBD = Submit V—| ΑΣΦ Determine the normal strain developed in wire BD. Provide Feedback Request Answer ΑΣΦ vec Request Answer vec SO ? ? mm/mm mm/mm Next >arrow_forward
- The strain components ɛx, ɛy, and Yxy are given for a point in a body subjected to plane strain. Using Mohr's circle, determine the principal strains, the maximum in-plane shear strain, and the absolute maximum shear strain at the point. Show the angle 0p, the principal strain deformations, and the maximum in-plane shear strain distortion in a sketch. Ex = 0 µɛ, ɛy = 430 µɛ, Yxy = 230 µrad. Enter the angle such that -45° s 0,s+45°. Answer: Ep1 με Ep2 = Ymax in-plane prad Yabsolute max. prad %3Darrow_forwardCompletely solve the problem. Box the final answer. Write legilby.arrow_forwardQ1arrow_forward
- 1.40 Given a major principal strain of 600µ and strain invariants I, = 400µ and I, = - 4800µ, find the remaining principal strains. Find, in magnitude and direction, the octahedral normal and shear strains. Answer: (1u = 1 x 10 ) 200p.- 400u. 133µ, 822uarrow_forwardHow can I draw in mohr's circle?arrow_forwardThe state of strain at the point on the arm in Figure Q10 has components ϵx = 200.5 micro-strain, ϵy = 324.4 micro-strain, and γxy = 220.6 micro-strain (1 micro-strain = strain×10-6). Figure 10 Calculate the maximum principal strain. Express your answer in micro-strains. Report your answer to 1 decimal place.arrow_forward
- A differential element on the bracket is subjected to plane strain that has the following components: , Ex = 300 x 10-6, Ey = 200 x 10-6, Exy = -500 x 10-6. Use the strain-transformation equations and determine the normal strain Ex' in the x' direction on an element oriented at an angle of 60°. Note, a positive angle is counter clockwise.arrow_forward! Required information Consider the given state of plane strain. Ex=-180µ, Ey=-260µ, Yxy=+295µ Use Mohr's circle to determine the orientation and magnitude of the principal strains. (Round the final answers to one decimal place.) The orientations are %3D The magnitudes are Ea 93arrow_forwardThe strain components Ex, Ey, and Yxy are given for a point in a body subjected to plane strain. Using Mohr's circle, determine the principal strains, the maximum in-plane shear strain, and the absolute maximum shear strain at the point. Show the angle 0p, the principal strain deformations, and the maximum in-plane shear strain distortion in a sketch. Ex = 0 μE, Ey = 310 με, Yxy = 280 μrad. Enter the angle such that -45° ≤ 0,≤ +45° Answer: Ep1 = Ep2 = Ymax in-plane = Yabsolute max. = 0p = με με urad uradarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY