
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Items in parentheses are the sol
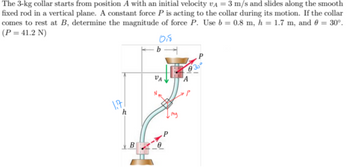
Transcribed Image Text:The 3-kg collar starts from position A with an initial velocity VA = 3 m/s and slides along the smooth
fixed rod in a vertical plane. A constant force P is acting to the collar during its motion. If the collar
comes to rest at B, determine the magnitude of force P. Use b = 0.8 m, h = 1.7 m, and 0 = 30°.
(P = 41.2 N)
b
018
VA
A
P
1.77
h
my
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Gggarrow_forwardBody U with mass 5m is stacked on the top body W with mass m, and released. The bodies are in contact along the frictionless interface at 45 to the vertical. The body U is in contact with the frictionless vertical wall. Body W lies on the floor with coefficient of friction u. Relevant h dimensions are shown in the figure. Express the results in U: 5m terms of given quantities: m, g, h and µ (except when u is given numerically). You need not evaluate sin 45° = cos 45° = 2/2. 45 1 Draw the free body diagrams for the two bodies. W: m Find the critical coefficient of friction µ. (i.e., the minimal coefficient friction to prevent sliding). 3h 31 Let uarrow_forwardThe man is trying to push the homogeneous 20-kg ladder AB up a wall by applying thehorizontal force P. The coefficient of static friction between the ladder and both contact surfaces is0.3. Determine the following:[1] the smallest value of P that would move the ladder[2] the total reaction at A and the reaction at Barrow_forward
- Determine the force P required to maintain the 200-kg engine in the position for which e = 300. The diameter of the pulley at B is %3D negligible ( take g=10 m/s2) 2 m 2 m OC 200 kg P= 1693.7 N O P= 1793.7 N O P=1993.7 N O P= 1893.7 N Oarrow_forwardA heavy crate with a weight of 160 lbs rests on a floor for which μS = 0.2. Find the minimum force P necessary for impending motion and determine whether the crate slides or tips, given:L1 = 4.4 ft, L2 = 2 ft, θ = 30 °arrow_forwardThe homogeneous cylinder A has a mass of 80 kg, and the mss of the hub can be neglected. The magnitude of the variable force P, is in newtons when t is in sec- onds. The velocity of body B changes from 2 m/s downward when t = 0 to 4 m/s downward t = 5 s. Determine the mass of B. Solve all questions using Impulse and Momentum methodsarrow_forward
- Determine the steady-state angle a if the constant force P = 115 N is applied to the cart of mass M = 24 kg. The cart travels on the slope of angle 0 = 20°. The pendulum bob has mass m = 7 kg and the rigid bar of length L = 1.5 m has negligible mass. Ignore all friction. %D P M L m Answer: a = iarrow_forwardHow to apply energy equation here . please include diagram. Don't use Artificial intelligence tools.arrow_forwardThe 6-kg bar is released from rest while in the position shown and its end rollers travel in the vertical-plane slot shown. If the speed of roller A is 3.42 m/s as it passes point C, determine the work done by friction on the system over this portion of the motion. The bar has a length /=775 mm. %3D Assume 0 = 24°. C (B Answer: Ufriction i N-marrow_forward
- h Can the statue be dragged without tipping? No Yes y = Movers are trying to set up an art gallery. They attempt to drag a human-size statue of a soda can with mass m = 120 kg by tying a rope around it. Determine if the movers can drag the statue along the floor without it tipping if the coefficients of static friction and kinetic friction are found to be μg = 0.38 and μ = 0.22, respectively. What is the maximum force the movers can apply without tipping the statue? The can has a height of h = 1.7 m and the rope is tied 1 m off the ground. Assume the statue to be a solid cylinder with radius r = 0.2 m and constant density. y F m 元 N Ftip If the movers can apply the force required for the statue to slip, where is the maximum height they should tie the rope to safely drag the statue?arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ...arrow_forwardDetermine the force P that will cause impending motion. Also determine location of the resultant force acting on the crate, measured from the point A. (M=200 kg, a=1 m, b=2m, c=0.5 m, d34, e=3 and coefficient of friction is 0.3) aarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY