
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781133949640
Author: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Testing a asking question.

Transcribed Image Text:1) mass of benzil = moles x molar mass of benzil
= 0.35 mmol x 210.232 g/mol
= 73.5812 x 10^-3 g
= 73.58 mg
mass of benzoin=0.35 mmol x 212.24 g/mol
= 74.284 x 10^-3 g
= 74.284 mg
2)
a) one mole of sodium borohydride (NABH4) can reduce four moles of aldehyde or
ketone
therefore
one mole of sodium borohydride (NaBH4) can reduce 2 moles of benzil because benzil
has 2 ketone group
and
for 0.35 mmol of benzil , moles of NABH4 required = 0.35 mmol / 2 = 0.175 mmol
thus
mass of NaBH4 = 0.175 mmol x 37.83 g/mol
= 6.62 mg
b) as we know that for 0.35 mmol of benzil , only 6.62 mg of NaBH4 is required
therefore
15 mg is very large and Only 0.35 mmol of benzil , leads to the result that
benzil is the limiting reagent.
3) the balanced reaction or the reaction of the NaBH4 with H2O is given as
NABH4 + 3 H20
NaH2BO3 + 4 H2
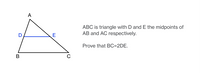
Transcribed Image Text:A
ABC is triangle with D and E the midpoints of
AB and AC respectively.
E
Prove that BC=2DE.
В
C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 9. In the graphic below we have two types of materials X and Y: i) a & b refer to material "X" in the absence of an external magnetic field and in the presence of magnetic field respectively. "c" refers to material "Y" with different domains having different orientations of electron spin and "d" refers to material "Y" under the influence of an external magnetic field. Identify whether (X or Y) is paramagnetic or ferromagnetic or neither. ii) ii) X: (a) (b) AAA. TTTTT Y: (c) (d)arrow_forwardWhat in Bacha'2H2O? 3 the true percen tage of weterarrow_forwardWould you expect a C¬C s bond formed by sp2–sp2 overlap to be stronger or weaker than a C¬C s bond formed by sp3–sp3 overlap?arrow_forward
- water Drew holedre interacting with each possible point of norecole. Use pekel cheres Cこarrow_forwardTramisol (shown below) is an anthelmintic used to control intestinal and lung worms in sheep and cattle. How many asymmetric centers are present in this structure? S ·N· Narrow_forwardstion 1 Consider the prochiral compound shown below. Is this the re or si face? re Osi 9 MacBook Air 80arrow_forward
- hat is meant by the term driving forces? Why are mailer spread and energy spread considered to be driving forces?arrow_forwardthe following figure shows the bond distances for the homonuclear diatomics of the 2 nd period p-block elements, as well as those for some of the ions derived from these species. i) Note that N 2 + has a longer bond distance than N 2, but O 2 + has a shorter bond distance than O 2. Explain this difference. ii) Estimate the bond distance of N 2 - and justify your answer.arrow_forward4. Draw the LCAO MO diagram of CO₂ and show its ground-state electron configuration using the D₂h point group (hint: find the LCAO MOs of O₂ first). Use the approximate relative energies of C and O orbitals below: E 2p 2s C O 2p 2s axes: X 0=C=0- Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning