
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
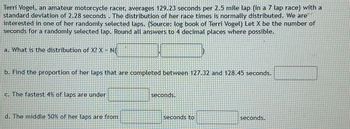
Transcribed Image Text:Terri Vogel, an amateur motorcycle racer, averages 129.23 seconds per 2.5 mile lap (in a 7 lap race) with a
standard deviation of 2.28 seconds. The distribution of her race times is normally distributed. We are
interested in one of her randomly selected laps. (Source: log book of Terri Vogel) Let X be the number of
seconds for a randomly selected lap. Round all answers to 4 decimal places where possible.
a. What is the distribution of X? X NO
b. Find the proportion of her laps that are completed between 127.32 and 128.45 seconds.
c. The fastest 4% of laps are under
d. The middle 50% of her laps are from
seconds.
seconds to
seconds.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Area Under a Normal Distribution Bin... THE SCORES OF A SCIENCE TEST HAD AN AVERAGE OF 78 AND A STANDARD DEVIATION OF 3. WHAT PERCENT OF STUDENTS SCORED ABOVE AN 82? THE SCORES ON A SCIENCE TEST HAD AN AVERAGE OF 78 AND A STANDARD DEVIATION OF 3. WHAT PERCENT OF STUDENTS SCORED BETWEEN A 69 AND 79? THE SCORES ON THE SAT MATH HAD A MEAN OF 431 AND A STANDARD DEVIATION OF 117. HOW HIGH OF A SCORE DO YOU NEED TO BE IN THE TOP 10% OF ALL SCORES?arrow_forwardFind the indicated IQ score. The graph to the right depicts IQ scores of adults, and those scores are normally distributed with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. The indicated IQ score, x, is(Round to one decimal place as needed.)arrow_forwardInternet Service Providers The amount that households pay service providers for access to the Internet varies quite a bit, but the mean monthly fee is $50 and the standard deviation is $20. The distribution is not Normal: many households pay a low rate as part of a bundle with phone or television service, but some pay much more for Internet only or for faster connections. A sample survey asks an SRS of 50 households with Internet access how much they pay. Let x be the mean amount paid. 1. Explain why you can't determine the probability that the amount a randomly selected household pays for access to the Internet exceeds $55. 2. What are the mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution of x ? 3. What is the shape of the sampling distribution of x ? Justify your answer. 4. Find the probability that the average fee paid by the sample of households exceeds $55.arrow_forward
- Terri Vogel, an amateur motorcycle racer, averages 129.52 seconds per 2.5 mile lap (in a 7 lap race) with a standard deviation of 2.28 seconds . The distribution of her race times is normally distributed. We are interested in one of her randomly selected laps. (Source: log book of Terri Vogel) Let X be the number of seconds for a randomly selected lap. Round all answers to 4 decimal places where possible. b. Find the proportion of her laps that are completed between 128.81 and 131.26 seconds c. The fastest 3% of laps are under ____ seconds. d. The middle 80% of her laps are from __________ seconds to __________ seconds.arrow_forwardFind the indicated IQ score. The graph to the right depicts IQ scores of adults, and those scores are normally distributed with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. Click to view page 1 of the table. Click to view page 2 of the table. CID The indicated IQ score, x, is. (Round to one decimal place as needed.) 0.99arrow_forwardSolve A through Farrow_forward
- The histogram has a longer tail/appears roughly the same/has a longer right tail so the distribution of the data is not skewed/skewed to the left/ skewed to the rightarrow_forwardPsychology students at a university completed the Dental Anxiety Scale questionnaire. Scores on the scale range from 0 (no anxiety) to 20 (extreme anxiety). The mean score was 11 and the standard deviation was 3.5. Assume that the distribution of all scores on the Dental Anxiety Scale is normal with u = 11 and o = 3.5. Complete parts a through c. Click here to view a table of areas under the standardized normal curve. a. Suppose you score a 18 on the Dental Anxiety Scale. Find the z-value for this score. z= 2 (Round to the nearest hundredth as needed.) b. Find the probability that someone scores between 10 and 15 on the Dental Anxiety Scale. P(10sxs 15) = (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. Find the probability that someone scores above 17 on the Dental Anxiety Scale. P(x> 17) =| (Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardP K @ 2 Listed in the data table are IQ scores for a random sample of subjects with medium lead levels in their blood. Also listed are statistics from a study done of IQ scores for a random sample of subjects with high lead levels. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations. Do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. Click the icon to view the data table of IQ scores. Help me solve this S a. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the mean IQ scores for subjects with medium lead levels is higher than the mean for subjects with high lead levels. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? Assume that population 1 consists of subjects with medium lead levels and population 2 consists of subjects with high lead levels. F2 W 30² OA H₂: #₁ = 1/₂ H₁: Hy #4₂ OC. Ho: Hy #4₂ H₁: Hy > H₂ The test statistic is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) mmand X…arrow_forward
- Find the standard deviation for the group of data items. 5, 6, 7, 7, 8, 9 The standard deviation is (Simplify your answer. Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardTerri Vogel, an amateur motorcycle racer, averages 129.69 seconds per 2.5 mile lap (in a 7 lap race) with a standard deviation of 2.25 seconds . The distribution of her race times is normally distributed. We are interested in one of her randomly selected laps. (Source: log book of Terri Vogel) Let X be the number of seconds for a randomly selected lap. Round all answers to 4 decimal places where possible.a. What is the distribution of X? X ~ N(,)b. Find the proportion of her laps that are completed between 127.93 and 130.17 seconds. c. The fastest 4% of laps are under seconds.d. The middle 60% of her laps are from seconds to seconds.arrow_forwardPsychology students in the Izmir University of Economics completed the Dental Anxiety Scale questionnaire in 2020. In this study, scores on the scale range from 0 (no anxiety) to 20 (extreme anxiety). The mean score was 14 and the standard deviation was 3.5. Assume that the distribution of all scores on the Dental Aroxiety Scale is normal with u= 14 and g=35. Complete parts a through c A Click here to view a table of areas under the standardized normal curve O Table of Normal Curve Areas a. Suppose you score a 18 on the Dental Anxiety Scale. Find the z-value for this score. z= (Round to the nearest hundredth as needed ) b. Find the probability that someone scores between 13 and 18 on the Dental Anxiety Scale P(13sxs 18) =D (Round to four decimal places as needed) c. Find the probability that someone scores above 17 on the Dental Anxiety Scale P(x> 17)=(Round to four decimal places as needed.) Enter your answer in each of the answer boxes. |8 目 國 100 |8 案 |8 業 可 0 | 会效 到商同 我目 |arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman