
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
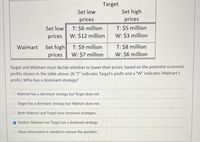
Transcribed Image Text:Target
Set low
Set high
prices
T: $6 million
W: $12 million
prices
T: $5 million
W: $3 million
Set low
prices
T: $8 million
W: $6 million
Set high
T: $9 million
W: $7 million
Walmart
prices
Target and Walmart must decide whether to lower their prices, based on the potential economic
profits shown in the table above. (A "T" indicates Target's profit and a "W" indicates Walmart's
profit.) Who has a dominant strategy?
O Walmart has a dominant strategy but Target does not.
Target has a dominant strategy but Walmart does not.
O Both Walmart and Target have dominant strategies.
O Neither Walmart nor Target has a dominant strategy.
More information is needed to answer the question.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose goods X and Y are complimentary products. Which of the following are correct with respect to the competitive market model of supply and demand? (check all that apply) an increase in the price of good Y will cause an increase in demand for good X and reduce the quantity demanded for good Y an increase in the price of good Y will cause a decrease in demand for good X and reduce the quantity demanded for good Y a decrease in the price of good X will increase the quantity demanded for good X and cause a decrease in demand for good Y a decrease in the price of good X will increase the quantity demanded for good X and cause an increase in demand for good Yarrow_forwardWalmart can be viewed as a first mover. Now suppose both Walmart and HEB are considering whether and how to enter a potential market. Market demand is given by the inverse demand function p= 900−q1−q2, where p is the market price margin, q1 is the quantity sold by Walmart and q2is the quantity sold by HEB. To enter the market, a retailer must build a store. Two types of stores can be built: Small and Large. A Small pantry store requires an investment of $50,000, and it allows the retailer to sell as many as 100 units of the goods at zero marginal cost. Alternatively, the retailer can pay $175,000 to construct a Large full-service supermarket that will allow it to sell any number of units at zero marginal cost. *Assume Walmart has built a Large full-service supermarket (i.e.Walmart chooses to build a large full-service supermarket L1 at the first stage). Calculate Walmart's profit for the following cases: a.) HEB chooses not to enter N at the second stage after viewing Walmart’s…arrow_forwardAnswer the c and d optionsarrow_forward
- Please explain as detail as possible, thanks.arrow_forwardQuestion 11. Consider the market for flounders (a sort of fish). The demand curve in the northern part of the country is given by QN (P) = 2000-100P while that in the southern part is Qs(P) = 5000-500P. The supply curve for the entire country is Q(P) = 20P. What is the market demand for the entire country (i.e., northern and southern part combined) at a price of P=11 (round to the nearest integer if needed)? a) Q = 199 b) Q =10 c) Q =900 d) Q = 400arrow_forwardAssume that the resource market is purely competitive. If the price of the resource falls, other factors constant, then a firm that sells its product in a purely competitive market will Multiple Choice increase production by a larger amount than a firm with some monopoly power in its product market. increase production by a smaller amount than a firm with some monopoly power in its product market. decrease production by a larger amount than a firm with some monopoly power in its product market. decrease production by a smaller amount than a firm with some monopoly power in its product market.arrow_forward
- The widget market is competitive and includes no transaction costs. Five suppliers are willing to sell one widget at the following prices: $26, $14, $10, $5, and $3 (one seller at each price). Five buyers are willing to buy one widget at the following prices: $10, $14, $26, $34, and $42 (one buyer at each price). For each price shown in the following table, use the given information to enter the quantity demanded and quantity supplied. Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied ($ per widget) (widgets) (widgets) $3 $5 $10 $14 $26 $34 $42 In this market, the equilibrium price will be per widget, and the equilibrium quantity will be widgets.arrow_forwardQUESTION 21 (Table: GoGo Gas and Fanny's Fantastic Fuel) Use Table: GoGo Gas and Fanny's Fantastic Fuel. The table shows a payoff matrix for GoGo Gas and Fanny's Fantastic Fuel in a small town. Each firm can set either a high price or a low price, and customers view both gas stations as nearly perfect substitutes. Profits in each cell of the payoff matrix are given as (GoGo's profit, Fanny's profit). If each firm sets the price independently, the Nash equilibrium outcome will be: Table: GoGo Gas and Fanny's Fantastic Fuel Fanny's Fantastic Fuel High Price S100, S100 $25, $150 $150, $25 Low Price High Price Low Price GoGo Gas $50, $50 O a $100, $100. b. $150, $25. c. $25, $150. d. S50, $50arrow_forwardNew Zealand possums produce the highest quality fur, due to the large pelts per body size. Demand for New Zealand possums’ products has risen dramatically. This is partly a result of the conservation benefits of harvesting New Zealand possums. This has made the product seem more environment friendly than other fur products and boosted sales to concerned consumers. Assume that the possums market satisfies all the attributes of a competitive market. Further assume that high grade possum furs are the most expensive input into the possum fur production function. 1. Use a graph of the market for possum fur to demonstrate the effect of its environmentally friendly status on the market equilibrium. 2. Graph the reaction of an individual incumbent firm to the increase in market demand. In your graph, identify the firm’s revenue and cost structures. 3. What would you predict would happen to long-run industry supply if the price of possum fur increased as possum culling increased their…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education