
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
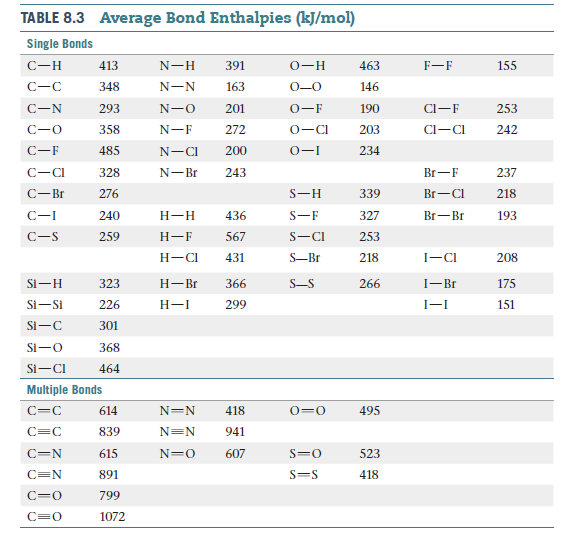
(a) Compare the bond enthalpies (Table 8.3) of the carbon–
carbon single, double, and triple bonds to deduce an average
π -bond contribution to the enthalpy. What fraction of
a single bond does this quantity represent? (b) Make a similar
comparison of nitrogen–nitrogen bonds. What do you
observe? (c) Write Lewis structures of N2H4, N2H2, and N2,
and determine the hybridization around nitrogen in each
case. (d) Propose a reason for the large difference in your
observations of parts (a) and (b).
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE 8.3 Average Bond Enthalpies (kJ/mol)
Single Bonds
C-H
413
N-H
391
О—н
463
F-F
155
348
N-N
163
0-0
146
293
201
0-F
190
CI-F
253
C-0
358
N-F
272
0-CI
203
Cl-CI
242
C-F
485
N-CI
200
0-I
234
C-CI
328
N-Br
243
Br-F
237
C-Br
276
S-H
339
Br-CI
218
C-I
240
Н-Н
436
S-F
327
Br-Br
193
C-S
259
Н—F
567
S-CI
253
Н—СІ
431
S-Br
218
I-CI
208
Si-H
323
Н—Br
366
S-S
266
I-Br
175
Si-Si
226
Н-I
299
I-I
151
Si-C
301
Si-O
368
Si-CI
464
Multiple Bonds
614
N=N
418
0=0
495
839
N=N
941
615
607
523
C=N
891
S=S
418
799
1072
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 11 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Example 8.3.2: Another Example of the Measurement of an Enthalpy Change A gummy bear contains 2.67 g sucrose, CaH»011. When it reacts with 7.19 g potassium chlorate, KCIO, 43.7k] of heat are produced. Determine the enthalpy change for the reaction CH,O,(ag) +8KCIO, (aq)- 12CO,(g) +11H,0(1) +8KCI(ag) Answer: Check 耳 日 自 LU (47) to searcharrow_forwarda) Using the balanced equation and the data in the table below, calculate the theoretical enthalpy of combustion. Note: you will need to include the enthalpy of vaporisation for the liquid components which are also given. CH3OH() +1.502(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O (1) Average Bond Enthalpies (kJ mol¹) C-H C-C C-O O=O C=O O-H Enthalpy of Vaporisation (kJ mol-¹) Methanol Water 412 348 358 496 743 463 35 41arrow_forwardConsider the following reactions: AH = -393.5 kJ (graphite) + 2 AH = -285.8 kJ 2(g) CH,OH + 3/2 0, +2H,0 AH = -726.4 k (1) Choose... Choose... -48.25 Calculate the enthalpy change for the following reaction: 188.7 + 2 H29) CH,OH -37.6 C (graphite) + V½ 0, 10.7 -238.7 39.0 268 11.85 Given the following information: N, bond energy = 941 kJ/mol, F, bond energy = 154 kJ/mol 2 N + 3/2 F AH = -103 kJ/mol 2(g) Choose... Calculate the N-F bond energy (kJ/mol) A ballon originally had a volume of 8.68 L at 258 K and a pressure of 575 mmHg. To what temperature (in K) must the balloon be cooled to reduce its volume to 5.00 L at a pressure of 730 mmHg? Choose... Varrow_forward
- Calculate the approximate enthalpy of the following reaction using the data below. 12 "C" atoms joined together in a cyclic (circular) structure with as many Hs connected so that each C atom has 4 bonds in total added to as many 02 atoms (which is O double bonded to another O) as would be required to react gives CO₂ which is a C double bonded to two O atoms and water which is O single bonded to 2 "H" atoms. This reaction needs to be balanced. Data for bond energies in kJ/mol : C single bond C is 347. C single bond H is 414. C double bond O is 736. O double bond O is 498. O single bond H is 464. The Correct answer is -5,736 Can someone explain how can I get to this answer with the steps.arrow_forwardQ. Use the average bond energy approach to calculate the enthalpy for the complete combustion of CH3OH(g).arrow_forwardHow much energy is required to break the bonds in the molecule of NO, BCl3, and NO2? and How do I find the ΔH of the molecule from the elements in their standard states?arrow_forward
- The heat gained by the solution in reaction two is 5.3 kJ. how many moles of NaOH were consumed ? what was the enthalpy of reaction ? (In kJ/mole)arrow_forwardFluorine (F2), the most electronegative element reacts with water in a different way compared to other halogens do. With excess water, fluorine reacts with water to produce hydrofluoric acid and oxygen gas in the following reaction: 2F2(g) + 2H2O() →4HF (1) + O2(g) Calculate AHrxn for the process above from the following information: AH= +571.6 kJ (a) AH= +542.0 kJ (b) 2H₂O(1)→ 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2HF (g) → H2(g) + F2(g) Which equation(s) will you flip? O a. Only equation (b) O b. Only equation (a) O c. Both equations will be flipped. O d. No equations will be flipped.arrow_forwardGiven that the average bond energies for C-H and C-Br bonds are 413 and 276 kJ/mol, respectively. Calculate the heat of atomization of bromoform (CHBr3) (kJ/mol) and show the calculation step.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY