
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Table 3 - Resistivity of Different Materials
Length of the wires: Q,240 m
Cross Sectional
Calculate
Theoretical
Diameter
Voltage
Current
Resistance
Percent
Area
Resistivity
Resistivity
(m)
(V)
(A)
( )
Error
( )
0.001016
0.00575
1.09775
0.001016
0.2934
0.96121
0.001016
0.2200
0.95525
Transcribed Image Text:Discussion:
Ohm's Law describes the relationship between the resistance (R) of a wire, the voltage drop across it (V), and current
through it (1):
V = RI
(1)
Applying a known current to a wire and measuring the voltage across it will let you determine the resistance of the
wire by solving equation 1:
(2)
The resistance of a particular element depends on its geometry, the resistivity and the temperature. Resistivity is the
tendency of the material to behave as a resistor and is an inherent property of a material, in the same sense that density or
thermal expansion are inherent properties. Materials with lower resistivity, like copper, are good conductors of electricity
and widely used in cireuit components while those with larger resistivity, like rubber, are used as insulators.
For a wire with length (L), cross-sectional area (A), and made from a material with resistivrity (p) the resistance (R)
will be given by the following equation:
R= ,L
(3)
In case that the geometry (length and cross sectional area) and the resistance of the wire is known, then is possible to
caleulate the resistivity solving equation 3:
RA
(4)
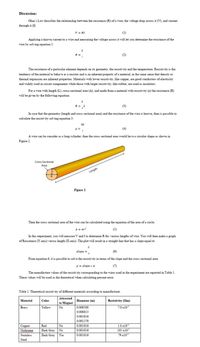
A wire can be consider as a long cylinder; then the cross sectional area would have a circular shape as shown in
Figure 2.
.
Cross Sectional
Area
Length
Figure 2
Then the cross sectional area of the wire can be caleulated using the equation of the area of a cirele:
A = mr?
(5)
In this experiment, you will measure V and I to determine R for various lengths of wire. You will then make a graph
of Resistance (Y-axis) versus length (X-axis). The plot will result in a straight line that has a slope equal to
slope =,
(6)
From equation 6, it is possible to solre the resistivity in terms of the slope and the cross sectional area:
p = slope + A
(7)
The manufacture values of the resistivrity corresponding to the wires used in the experiment are reported in Table 1.
These values will be used as the theoretical when caleulating percent error.
Table 1. Theoretical resistivity of different materials according to manufacturer.
| Attracted
to Magnet Dinmeter (m)
No
Material
Color
Resistivity (Qm)
7.0 x10*
Brass
Yellow
0.000508
0.000813
0.001016
0.001270
Copper
Nicbrome
No
Dark Gray No
Dark Gray
1.8 x10*
105 x10
79 x10
Red
0.001016
0.001016
Stainless
Yes
0.001016
Steel
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A current i (conventional current) flows through a ohmic resistance R as shown below. As the current flows to the right, R LN -WW O the voltage increases by iR the voltage decreases by iR O the voltage does not change none of the abovearrow_forwardUse the tables below as needed to solve this problem. TABLE 30.1 Conduction-electron TABLE 30.2 Resistivity and conductivity of conducting density in metals materials Resistivity (N m) Conductivity (N-'m-') Electron Metal density (m-) Material 6.0 x 1028 2.8 x 10 Aluminum Aluminum 3.5 x 107 8.5 x 10 1.7 X 10 2.4 x 10" 9.7 x 10" 1.6 x 10 5.6 X 10* 1.5 x 10 3.5 x 10 Copper Соpper 6.0 × 107 Iron 8.5 x 1028 Gold 4.1 x 107 Gold 5.9 × 1028 Iron 1.0 x 10 Silver 5.8 x 1028 Silver 6.2 x 107 1.8 x 10 e en Tungsten Nichrome* 6.7 x 10 Carbon 2.9 x 10 *Nickel-chromium alloy used for heating wires. Pure aluminum is malleable, which means that it can be pounded or stretched into different shapes. You are given a small aluminum cube, with side length 5.0 mm. The goal is to shape this cube so that 2.0 A current flows through it when connecting the two ends to the terminals of 12 V battery. a) To what cross-sectional area A and length L should you stretch the cube, and how should the battery be…arrow_forwardContent Material Aluminum Copper Gold Iron Platinum Silver Tungsten Problem Resistivity (22.m) 2.65 x 10-8 1.68 x 10-8 2.44 x 10-8 9.71 x 108 10.6 x 10-8 1.59 x 10-8 5.60 x 10-8 As shown below, an insulated tungsten wire is immersed in 398 g of water at 12 °C. The wire is 1.9 cm long and has a cross-sectional area of 0.006 cm². wire A.) Determine how much heat is needed to bring the water to a boil. The specific heat of water is 4186 J/kg.K. Q = B.) Determine how long it will take to bring the water to a boil if a 13 A current is run through the wire. Assume all the thermal energy generated by the wire is absorbed by the water. At =arrow_forward
- 1)What is resistivity of wire? 2)Rnew = ? 3) Inew = ?arrow_forwarda) Calculate the intensity of electric current passing through the resistance of 4ohms. b) Calculate the voltage at the resistance of 2 ohms.arrow_forwardIf each of the resistors has a value of 4 ohms, then the equivalent resistance of this circuit is R, R3 Reg = ? %3D R5 16 ohms OA OB 7 ohms oc 12 ohms OD 20 ohms OE 4 ohmsarrow_forward
- What is the total resistance in the circuit below? R2 = 242 R3 = 82 E = 30 V2 R = 42 O 10 ohms O 36 ohms 26.6 ohms O 28 ohmsarrow_forward2) A wire has a diameter of 10mm, length 50m and resistivity 3.8 x 10^-8 ohm metres. What is the resistance of the wire?arrow_forwardHow to solve this questionarrow_forward
- Which equation will give you the current flowing through a wire if you are given the voltage and resistance in a circuit? P=1?R V=IR Fq=kq,q;/d? P=VIarrow_forwardCircuit Problem: Express each labelled voltage and current (e.g., vx, ix) in terms of the resistances and source currents and voltages (e.g., R0).arrow_forwardR= PL A resistance = 0.667 ohms P L A resistivity length area 0.50 10.00 7.50 cm cm cm²arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON