
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
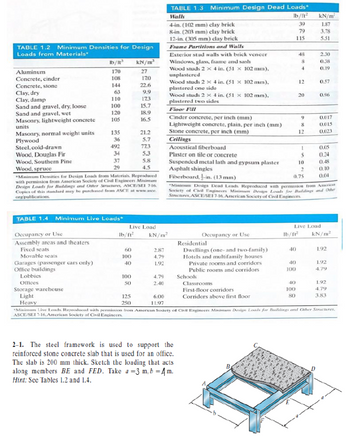
Transcribed Image Text:TABLE 1.2 Minimum Densities for Design
Loads from Materials
Aluminum
Concrete, cinder
Concrete, stone
Clay, dry
Clay, damp
Sand and gravel, dry, loose
Sand and gravel, wet
Masonry, lightweight concrete
units
Masonry, normal weight units
Plywood
Steel, cold-drawn
Wood, Douglas Fir
Wood, Southern Pine
Wood, spruce
Occupancy or Use
Assembly areas and theaters
Fixed seats
Movable seats
Garages (passenger cars only)
Office buildings
170
108
Lobbies
Offices
144
63
110
TABLE 1.4 Minimum Live Loads*
Storage warehouse
Light
Heavy
100
120
105
135
36
492
34
37
29
*Minimum Densities for Design Loads from Materials. Reproduced
with permission from American Society of Civil Engineers Misimam
Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures, ASCE/SEI 7-16.
Copics of this standard may be purchased from ASCE at www.ace.
org/publications.
lb/ft²
60
100
40
kN/m²
27
170
22.6
9.9
173
15.7
Live Load
100
50
18.9
16.5
125
250
21.2
5.7
773
5.3
5.8
4.5
kN/m²
2.87
4.79
1.92
4.79
2.40
6.00
11.97
TABLE 1.3
Walls
4-in. (102 mm) clay brick
8-in. (203 mm) clay brick
12-in. (305 mm) clay brick
Frame Partitions and Walls
Minimum Design Dead Loads*
lb/ft²
39
79
Exterior stud walls with brick vencer
Windows, glass, frame and sash
Wood studs 2 x 4 in. (51 x 102 mm).
unplastered
Wood studs 2 x 4 in. (51 x 102 mm),
plastered one side
Wood studs 2 x 4 in. (51 x 102 mm),
plastered two sides
Floor Fill
Cinder concrete, per inch (mm)
Lightweight concrete, plain, per inch (mm)
Stone concrete, per inch (mm)
2-1. The steel framework is used to support the
reinforced stone concrete slab that is used for an office.
The slab is 200 mm thick. Sketch the loading that acts
along members BE and FED. Take a =3 m, b = 4 m.
Hint: See Tables 1.2 and 1.4.
Occupancy or Use
Residential
Dwellings (one- and two-family)
Hotels and multifamily houses
Private rooms and corridors
Public rooms and corridors
Schools
Classrooms
First-floor corridors
Corridors above first floor
115
Ceilings
Acoustical fiberboard
Plaster on tile or concrete
Suspended metal lath and gypsum plaster
Asphalt shingles
Fiberboard, -in. (13 mm)
"Mininum Desigs Dead Leads Reproduced with permission from America
Society of Civil Engineers Minimun Design Loads for Buildings and Other
Structures, ASCE/SEI 7-16 American Society of Civil Engineers
40
48
8
4
12
40
100
20
10
2
0.75
40
100
80
9
8
12
lb/f²2²
1
5
kN/m²
1.87
3.78
5.51
2.30
0.38
0.19
0.57
Live Load
0.96
0.017
0.015
0,023
0.05
0.24
0.48
0.10
0.04
kN/m²
1.92
1.92
4.79
1.92
4.79
3.83
*Minimum Live Loads. Reproduced with permission from American Society of Civil Engineers Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures.
ASCE/SEI 7-16, American Society of Civil Engineers.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4.7 The cross section of a conventionally reinforced concrete one-way slab is shown below. Using ACI Table 9.5(a), answer the following questions: 5'-0" CANTILEVER TI 23-0 END-BAY T2 SPAN L3 INTERIOR-BAY a. What is the minimum slab thickness at end bays (T2)? Member Solid one- way slabs BM WIDTH Beams or ribbed one- way slabs TABLE 9.5(a)- - MINIMUM THICKNESS OF NONPRESTRESSED BEAMS OR ONE-WAY SLABS UNLESS DEFLECTIONS ARE CALCULATED Simply supported 23-0 END-BAY 12 €/16 CANTILEVER Minimum thickness, h Both ends One end continuous continuous Cantilever Members not supporting or attached to partitions or other construction likely to be damaged by large deflections 1/20 024 U/28 U/10 d/18.5 (21 €/8 Notes: Values given shall be used directly for members with normalweight concrete and Grade 60 reinforcement. For other conditions, the values shall be modified as follows: a) For lightweight concrete having equilibrium dersity, we, in the range of 90 to 115 loft, the values shall be multiplied…arrow_forwardNote: kindly give me both right solutions according to the question.arrow_forwardWhat part of the building that uses concrete in which a sample of it must be brought to theTesting lab for examination or testing.arrow_forward
- TABLE 1.2 Minimum Densities for Design Loads from Materials Aluminum Concrete, cinder Concrete, stone Clay, dry Clay, damp Sand and gravel, dry loose Sand and gravel, wet Masonry, lightweight concrete Masonry, normal weight units Steel, cold-drawn Wood, Douglas Fir Wood, Southern Pine Wood, spruce AN/w 27 120 22.6 123 15.7 18.9 165 21.2 5.7 723 5.3 5.8 45 TABLE 1.3 Minimum Design Dead Loads From Paris and Walls Wood 1x plated Woodplatered Woodst 51x32mm, platered Cindere per Lightweight complaine Ceilings Aucuntic Shond Spendedahand Angle 5.54 9.57 2017 005 8:24 0.41 904 TABLE 1.4 Minimum Live Loade Oorspany or Use Amely Fixed seats and at Garage (can only) Officeday Lebbin Love Load 4.79 192 4.79 VEST S Occupancy or Use Dwelings (one-and two-mily) Hotels and many bo Private and don Campos Fint Coor comidon Comidon abfint floor Live Lead KN/² 190 4.39 3.33arrow_forwardQ) Differentiate b/w the following: A ) UBC & IBC. Subject: Reinforced concrete design iiarrow_forwardHow to determine if it is Singly Reinforced Beam or Doubly Reinforced Beam using the NSCP 2015?arrow_forward
- Define thixotropy phenomenon and how it is beneficial for construction situations?arrow_forwardcalculate a wall formwork pressure for a 20 foot concrete wall pour. A 20% fly ash blended cement concrete at 50 degrees will be used and the project intends to place the concrete in 3 equal lifts over 4 hours.arrow_forwardI need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forward
- Answer ASAP pls with well detailed solution. Thank you!arrow_forwarda. Describe in 2 paragraphs the use of Moisture Meter for wood testiing b. Describe in 2 paragraphs the use of Impact soil testerarrow_forwardURGENT Please answer this problem in 1 hour. Topic is 'Analysis/design of T-beams' in Principles of Reinforced/Prestressed Concrete. I need correct answers with complete and step by step solution. Box the final answers. Do not shortcut your solution. I will give an upvote if it satisfies. Thank you!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning