
Please write and show the balanced
Hint:
Experimental Procedure:
A. Preparation of 0.01M EDTA solution
Transfer about 2-g of disodium dihydrogen EDTA dihydrate and 0.1-g of MgCl2•6H2O into a clean 400-mL beaker and dissolve the solids in water. If the solution appears turbid, add NaOH solution until the solution is clear. Transfer the solution into an amber bottle, add enough distilled water to make about 0.500 L and mix thoroughly. Label the contents of the bottle as 0.01 M EDTA.
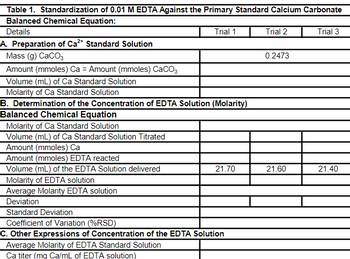
B. Standardization of 0.01M EDTA solution using CaCO3 as Primary Standard
You should prepare the Ca2+ standard solution as follows: accurately weigh about 0.2-0.4-g of primary standard CaCO3 that has been previously dried at 100oC. Transfer the solid to a 250-ml volumetric flask, using about 100-mL water. Slowly add 1:1 HCl dropwise until effervescence ceases and the solution is clear. Dilute with water to the mark and mix solution thoroughly. Pipet a 25-mL portion of the Ca2+ standard solution and transfer it into a 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask. Add 5-mL of the NH3-NH4Cl buffer solution and 5 drops of Eriochrome Black T (EBT) indicator. Titrate carefully with the EDTA solution to the point where the color changes from wine-red to pure blue. No tinge of red should remain in the solution. Repeat the titration with two other aliquots of Ca2+ standard solution.
Report the molar concentration of the EDTA solution.
C. Determination of Ca in Drugs
The Lab Instructor will provide you with an OTC drug sample that contains calcium lactate only and some information regarding the composition of the drug. From this data, make the detailed procedure for the determination of Ca in the drug sample. Always remember that the desired volume of the titrant that will be consumed for each analysis must lie within the range of 10 to 40 mL. Show the calculations to your Lab Instructor before proceeding.
Measure about 50 mL of distilled water into a 250-mL beaker and dissolve one or more tablets. If the sample is not very soluble in distilled H2O, add about 5 mL of 0.5 M HCl and this will improve its solubility. Transfer the dissolved tablet into a volumetric flask and dilute to the mark. Label the mixture as dilute tablet solution (DTS). Determine the volume of the aliquot portion of the DTS that must be measured so that the volume of the titrant needed to reach the end point will lie within the range of 10 to 40 mL.
With the use of a volumetric pipet, obtain an aliquot portion of the DTS and transfer it into a 250-mL Erlenmeyer flask. Add 1.0 mL of the buffer solution and 5 drops of the indicator solution. Titrate with the standard EDTA solution to a color change of wine-red to pure-blue. Perform the titration in triplicate measurements.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

- A sample of steel (0.1005 g) was dissolved in acid and the solution made up to 100 cm³ with demineralised water. From this solution, 10.0 cm³ aliquots, to which were added 0.0, 10.0, 20.0, 30.0, and 40.0 cm³ of a 2.50 mg L-1 Cr solution and the flasks made up to 100.0 cm³ with distilled water. Use the absorbance values obtained below for these solutions to determine the chromium content of the sample of steel, expressing the result as a weight percentage (% w/w). 3 Sample solution (10.0 cm³) + 0.0 cm³ standard Sample solution (10.0 cm³) + 10.0 cm³ standard Sample solution (10.0 cm³) + 20.0 cm³ standard Sample solution (10.0 cm³) + 30.0 cm³ standard Sample solution (10.0 cm³) + 40.0 cm³ standard Absorbance 0.201 0.292 0.378 0.467 0.554arrow_forwardc. Use the Table to answer the questions below Concentration (M) Absorbances 0.20 0.36 0.40 0.50 0.60 0.65 0.80 0.75 Plot the graph and attach your plot. Use the table to answer the following question i. If 1.1 cm cell was used. Calculate the molar absorptivity of Cr(Il). ii. What is the concentration of a compound with absorbance 0.60, if 2 cm cell is used.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- A 25.00-mL sample containing Ni2+ was treated with 25.00 mL of 0.5000 M EDTA to complex all the Ni2+ and leave excess EDTA in solution. The excess EDTA was then back titrated, requiring 7.11 mL of 0.450 M Zn2+. What was the concentration of Ni2+ in the original solution (keep 4 SF)?arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction. O + 0 CHBr3 Draw the major organic product formed in this reaction. 81 + [**** (CH3)3CO¹K+ • Use the wedge/hash bond tools to indicate stereochemistry where it exists. • Include H atoms at chiral centers only. • Show stereochemistry in a meso compound. If the reaction produces a racemic mixture, just draw one stereoisomer. - √n [F] ?arrow_forward25.00 mL 0.01000 M Ni2+ is titrated with 0.01000 M EDTA in a solution buffered topH 5.0. Given that the formation constant for the Ni-EDTA (NiY2–) chelate is4.2 x 1018 and the 4 value at pH 5.0 is 3.54 x 10–7. Explain briefly why EDTA is an important reagent used in complexometrictitrations.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





