
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
T = 23
The expression you should be evaluating for the number of moles (nn) is:
n=PV/RT
Where:
- P is in atm
- V is in L
- T is in K
- R = 0.0820574 L atm / mol K
need 6 sig figs

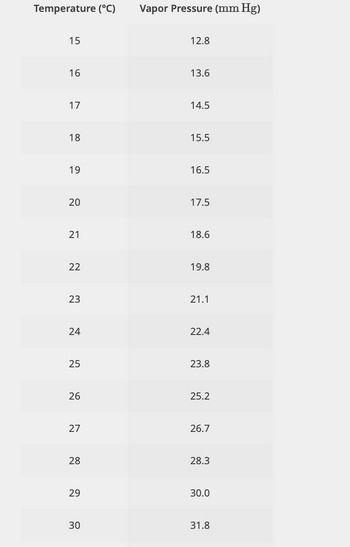
Transcribed Image Text:Using Figure 1 as reference, please complete the table below.
Remember that the volume of gas in your buret includes the uncalibrated volume of your buret and the volume that results from
subtracting the direct volume reading from 25.00 mL.
Trial #
1
2
3
V₁ (mL)
0.401989
0.401989
0.401989
Where:
x(mL)
11.00
10.00
10.00
V
gas = 25.00 − x +Vu
Vgas = Volume of gas in the buret (mL)
* = Final buret reading at the end of electrolysis time (mL)
V₁ = Volume of uncalibrated region of the buret (mL)
Gas constant = 0.0820574 L atm/mol K
Unrounded
14.40198
15.40198
Vgas (ml)
15.40198
Rounded
14.40
15.40
15.40
Moles of H₂ evolved
Unrounded
999
3
3
Rounded
P
3
3
3
Transcribed Image Text:Temperature (°C)
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
Vapor Pressure (mm Hg)
12.8
13.6
14.5
15.5
16.5
17.5
18.6
19.8
21.1
22.4
23.8
25.2
26.7
28.3
30.0
31.8
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Given data
The temperature is T = 23 °C = (273+23) K = 296 K.
The pressure is P = 21.1 mmHg = atm.
The universal gas constant value is R = 0.0820574 L.atm/mol.K.
We have to calculate the number of moles of hydrogen at different volumes.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the following equation, how would you increase the amount of product? UF4(g) + 2H2O(g) ↔↔ UO2(s) + 4HF(g) ΔH = -2104 kJ/mole A) Increase PUF4, increase PH2O, decrease temperature, decrease PHF, decrease total pressure. B) Increase PUF4, increase PH2O, increase temperature, decrease PHF, decrease total pressure. C) Increase PUF4, increase PH2O, decrease temperature, remove UO2, decrease PHF, increase total pressure. D) Increase PUF4, increase PH2O, increase temperature, decrease PHF, increase total pressure. E) Increase PUF4, increase PH2O, decrease temperature, decrease PHF, increase total pressure. F) Increase PUF4, increase PH2O, increase temperature, remove UO2, decrease PHF, increase total pressure. G) Increase PUF4, increase PH2O, increase temperature, remove UO2, decrease PHF, decrease total pressure. H) Increase PUF4, increase PH2O, decrease temperature, remove UO2, decrease PHF, decrease total pressure.arrow_forwardI need help with 15.37arrow_forwardThe decomposition of potassium chlorate produces oxygen gas: 2 KClO3(g) \rightarrow→ 2 KCl(s) + 3 O2(g) What volume of O2(g) (in liters) is produced by the decomposition of 178.9 g of KClO3(s) at T = 298 K and P = 1.00 atm? Given molar masses: KClO3: 122.55 g/mol; KCl: 74.551 g/mol; O2: 31.999 g/mol Enter the numerical value (no units) using 3 significant figures. Answer valuearrow_forward
- ▼ standard conditions Express your answer in kilojoules. AGixn = Submit Part B AGrxn= at equilibrium Express your answer in kilojoules. Submit Part C Π| ΑΣΦ AGrxn= Request Answer Submit IVE ΑΣΦ PICI = 2.58 atm ; P1₂ = 0.324 atm; Pcl₂ = 0.216 atm. Express your answer using one significant figure. Request Answer 17| ΑΣΦ Request Answer ? ? ? kJ kJ kJarrow_forward8arrow_forwardAs you are walking across your laboratory, you notice a 5.25 L flask containing a gaseous mixture of 0.0205 mole NO2 (9) and 0.750 mol N2O4 (q) at 25°C. 4 (g) Is this mixture at equilibrium? If not, will the reaction proceed towards forming more products, or more reactants? N2O4 4 (9) → 2NO2 (9) Ko = 4.61 x 103 at 25°Carrow_forward
- 3saarrow_forward5:53 A) Ne (g) B) O₂ (g) Question 2 of 15 Which one of the following would have the smallest value of Sº? C) A mixture of Ne and O₂ D) CO₂ (g) ..ll 5GW Tap here or pull up for additional resources Submitarrow_forwardAt a certain temperature, 0.389 mol CH4 and 0.606 mol H₂S are placed in a 3.00 L container. CH₂(g) + 2 H₂S(g) = CS₂(g) + 4H₂(g) At equilibrium, 12.3 g CS₂ is present. Calculate Kc. 2 Вс =arrow_forward
- Carbon disulfide is prepared by heating sulfur and charcoal. The chemical equation is S₂(g) + C(s) CS₂(g) Kc = 9.40 at 900 K How many grams of CS₂(g) can be prepared by heating 13.4 mol S₂(g) with excess carbon in a 5.65 L reaction vessel held at 900 K until equilibrium is attained? mass of CS₂(g): 6.0 garrow_forwardIn a certain experiment 7.50 mile of NH3 was placed in an empty 1.0 liter flask at 900C. After equilibrium was reached, 0.50 mile of N2 was found to be in the flask (along with other gases). Calculate the [NH3] and [H2] at equilibrium and the numerical value of Kc. 2NH3 (g) = N2(g) + 3H2(g)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY