
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:"Synthesis gas" is a mixture of carbon monoxide and water vapor. At high temperature synthesis gas will form carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and in fact this
reaction is one of the ways hydrogen is made industrially.
A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 1.5 L flask with 0.93 atm of carbon monoxide gas and 3.2 atm of water vapor. When the mixture has come to
equilibrium she determines that contains 0.62 atm of carbon monoxide gas, 2.89 atm of water vapor and 0.31 atm of hydrogen gas.
The engineer then adds another 0.23 atm of carbon monoxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the pressure of carbon dioxide
after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
atm
x10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
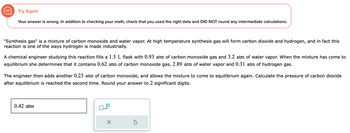
Transcribed Image Text:Try Again
Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations.
"Synthesis gas" is a mixture of carbon monoxide and water vapor. At high temperature synthesis gas will form carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and in fact this
reaction is one of the ways hydrogen is made industrially.
A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 1.5 L flask with 0.93 atm of carbon monoxide gas and 3.2 atm of water vapor. When the mixture has come to
equilibrium she determines that it contains 0.62 atm of carbon monoxide gas, 2.89 atm of water vapor and 0.31 atm of hydrogen gas.
The engineer then adds another 0.23 atm of carbon monoxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the pressure of carbon dioxide
after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
0.42 atm
x10
X
Ś
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Try Again
Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations.
"Synthesis gas" is a mixture of carbon monoxide and water vapor. At high temperature synthesis gas will form carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and in fact this
reaction is one of the ways hydrogen is made industrially.
A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 1.5 L flask with 0.93 atm of carbon monoxide gas and 3.2 atm of water vapor. When the mixture has come to
equilibrium she determines that it contains 0.62 atm of carbon monoxide gas, 2.89 atm of water vapor and 0.31 atm of hydrogen gas.
The engineer then adds another 0.23 atm of carbon monoxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the pressure of carbon dioxide
after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
0.42 atm
x10
X
Ś
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- "Synthesis gas" is a mixture of carbon monoxide and water vapor. At high temperature synthesis gas will form carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and in fact this reaction is one of the ways hydrogen is made industrially. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 500. mL flask with 0.82 atm of carbon monoxide gas and 0.85 atm of water vapor. When the mixture has come to equilibrium she determines that it contains 0.33 atm of carbon monoxide gas, 0.36 atm of water vapor and 0.49 atm of hydrogen gas. The engineer then adds another 0.41 atm of carbon monoxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the pressure of carbon dioxide after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. atmarrow_forward"Synthesis gas" is a mixture of carbon monoxide and water vapor. At high temperature synthesis gas will form carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and in fact this reaction is one of the ways hydrogen is made industrially. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 2.0 L flask with 3.1 atm of carbon monoxide gas and 3.6 atm of water vapor. When the mixture has come to equilibrium she determines that it contains 1.0 atm of carbon monoxide gas, 1.5 atm of water vapor and 2.1 atm of carbon dioxide. The engineer then adds another 0.90 atm of water, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the pressure of hydrogen after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 0 atm x10 C [arrow_forwardNitrogen dioxide is one of the many oxides of nitrogen (often collectively called "NOx") that are of interest to atmospheric chemistry. It can react with itself to form another form of NOx, dinitrogen tetroxide. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 1.5 L flask with 0.88 atm of nitrogen dioxide gas. When the mixture has come to equilibrium she determines that it contains 0.50 atm of nitrogen dioxide gas. The engineer then adds another 0.22 atm of nitrogen dioxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the pressure of dinitrogen tetroxide after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 0 atm ☐x10 X Śarrow_forward
- Steam reforming of methane ( CH,) produces "synthesls gas," a mixture of carbon monoxlde gas and hydrogen gas, which Is the starting polnt for many 4 Important industrial chemical syntheses. An Industrial chemist studying this reaction fills a 2.0 L flask with 4.7 atm of methane gas and 2.3 atm of water vapor, and when the mixture has come to equilibrium measures the partial pressure of hydrogen gas to be 4.1 atm. Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant for the steam reforming of methane at the final temperature of the mixture. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = || Check Explanation 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Accessib M 9 hp Cearrow_forward"Synthesis gas" is a mixture of carbon monoxide and water vapor. At high temperature synthesis gas will form carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and in fact this reaction is one of the ways hydrogen is made industrially. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 200. mL flask with 3.6 atm of carbon monoxide gas and 2.5 atm of water vapor. When the mixture has come t equilibrium she determines that it contains 2.0 atm of carbon monoxide gas, 0.90 atm of water vapor and 1.6 atm of carbon dioxide. The engineer then adds another 1.2 atm of carbon monoxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the pressure of hydrogen after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. atm x10arrow_forwardating UP bunE Ammonia has been studied as an alternative "clean" fuel for internal combustion engines, since its reaction with oxygen produces only nitrogen and water vapor, and in the liquld form It is easily transported. An Industrial chemist studying this reaction fills a 200. mL flask with 1.6 atm of ammonia gas and 4.7 atm of oxygen gas, and when the mixture has come to equilibrium measures the partial pressure of water vapor to be 1.7 atm. Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant for the combustion of ammonia at the final temperature of the mixture. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = Check Explanation 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Accessibility M 9 hp escarrow_forward
- At a certain temperature, 0.3011 mol of N₂ and 1.781 mol of H₂ are placed in a 4.00 L container according to the following equation: N₂(g) + 3H2(g) + 2NH3(g) At equilibrium, 0.1401mol of N₂ is present. Calculate the equilibrium constant.arrow_forward"Synthesis gas" is a mixture of carbon monoxide and water vapor. At high temperature synthesis gas will form carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and in fact this reaction is one of the ways hydrogen is made industrially. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 1.5L flask with 2.9 atm of carbon monoxide gas and 2.9 atm of water vapor. When the mixture has come to equilibrium she determines that it contains 1.4 atm of carbon monoxide gas, 1.4 atm of water vapor and 1.5 atm of carbon dioxide. The engineer then adds another 0.97 atm of carbon monoxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the pressure of hydrogen after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. atm x10 Submit Assignment Continue 2021 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accessibility MacBook Air DII 888 F10 F8 F9 esc F6 F7 F4 F5 F3 F2 %23 $4 % - & 4. 5 8.arrow_forwardAmmonia will decompose into nitrogen and hydrogen at high temperature. An industrial chemist studying this reaction fills a 200. mL flask with 4.6 atm of ammonia gas, and when the mixture has come to equilibrium measures the partial pressure of hydrogen gas to be 4.8 atm. Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant for the decomposition of ammonia at the final temperature of the mixture. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forward
- this one is asking for atmarrow_forwardNitrogen dioxide is one of the many oxides of nitrogen (often collectively called "NOX") that are of interest to atmospheric chemistry. It can react with itself to form another form of NOx, dinitrogen tetroxide. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 2.0 L flask with 2.9 atm of nitrogen dioxide gas. When the mixture has come to equilibrium he determines that it contains 1.4 atm of nitrogen dioxide gas. The engineer then adds another 1.5 atm of nitrogen dioxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the pressure of dinitrogen tetroxide after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. atm ☐ x10 Xarrow_forwardAt a certain temperature, 0.3811 mol of N₂ and 1.761 mol of H₂ are placed in a 4.50 L container according to the following equation: N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) + 2NH3(g) At equilibrium, 0.1001mol of N2 is present. Calculate the equilibrium constant.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY