
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
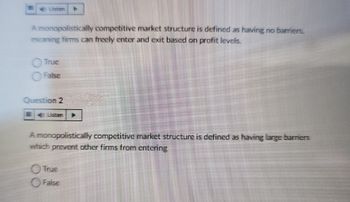
Transcribed Image Text:A monopolistically competitive market structure is defined as having no barriers.
meaning firms can freely enter and exit based on profit levels.
Question 2
A monopolistically competitive market structure is defined as having large barriers
which prevent other firms from entering
True
False
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 7 As competitors enter a monopolistically competitive industry, the incumbent firms' demand curves... Group of answer choices Shift to the left and become less elastic Shift to the right and become less elastic Shift to the left and become more elastic Shift to the right and become more elasticarrow_forwardQuestion 36 There are complete barriers to entry in monopolistic competition. True Falsearrow_forwardAnsarrow_forward
- A firm in a monopolistically competitive market has a monopoly power because: O There are very few other sellers in the market. There are many firms selling similar products. The firm is not concerned with entry of new firms. The firm's product is differentiated. ◄ Previous MAY 4 Next Not saved Submit tvarrow_forwardWhich of the following is not a difference between perfect competition and monopolistic competition? The monopolistic competitor faces a downward sloping demand curve. Long run economic profit. Excess capacity. Mark up over marginal cost. « < Question 6 of 40 A Moving to another question will save this response. Close Windowarrow_forwardIn what sense do monopolistically competitive firms have market power? Question 1Answer a. Firms in the long run will earn zero economic profits b. The demand curve that a typical firm faces is negatively sloped c. Because of brand loyalty, a firm can raise the price of its product without worrying that any of its customers will switch to buy other similar brands d. All of the answers are correctarrow_forward
- 17. Demand is given by Q = 220 P. Marginal cost is $120. Calculate the market equilibrium price, output, and any profits for: a. b. C. a monopoly context ? a Bertrand duopoly a Cournot duopolyarrow_forwardplease answer in text form and in proper format answer with must explanation , calculation for each part and steps clearlyarrow_forwardEOC 17.03 (and 17.04) As new businesses enter a monopolistically competitive market, what happens to profits of existing businesses and product diversity in the market? Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a profits of existing firms rise and product diversity in the market increases. b. profits of existing firms rise and product diversity in the market decreases. profits of existing firms decline and product diversity in the market increases. d. profits of existing firms decline and product diversity in the market decreases.arrow_forward
- If members of an oligopolistic industry wish to maximize profits for the industry, they will likely charge prices that are what a monopoly would charge and all together produce a quantity that is what a monopoly will produce. Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a b с Question 13 Homework. Unanswered Due Today, 11:59 PM d greater than; equal to equal to; higher than greater than; higher than equal to; equal to Unanswered Submitarrow_forward1) Are monopolists guaranteed of making economic profits?. pleas explain.2) Explain the long run equilibrium situation for a monopolistically competitive industry. Give two examples of industries that fit under this category.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education