
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Suppose you gathered a ball of interstellar gas that was
equal to the size of the Earth (a radius of about 6400 km). If
this gas has a density of 2.8 hydrogen atoms per cm3, typical
of the interstellar medium, what would its total mass be?
(For comparison, a bowling ball has a mass of about 5 kg)
(HINT: 2.8 hydrogen atoms per cm3
corresponds to a density
of 4.68 × 10−21 kg/m3)
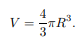
Transcribed Image Text:4
V =
3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- describe in detail why and in what situation you use mgh=1/2kx^2, and the question (why it is looking like this?)arrow_forward(a) Rank the following components of the interstellar medium in order of the wavelengths at which they are observed, longest wavelength first: clouds of neutral hydrogen, coronal gas, interstellar dust, nebulae. Longest to Shortest? (b) Rank the same material in order of decreasing temperature from hottest to coolest. Hottest to Coolest?arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements best describes our galaxy, the Milky Way? O A bulge dominated system, with little or no disk, approximately 27,000 light years across. A disk 100,000 lightyears across filled with gas and stars, with a bulge of older stars in the galaxy centre. A disk 27,000 light years across with a bulge of gas and newly formed stars in the galaxy centre. O A spherical (elliptical) galaxy, 100,000 lightyears across, with no gas and no new stars.arrow_forward
- In a globular cluster, astronomers (someday) discover a star with the same mass as our Sun, but consisting entirely of hydrogen and helium. Is this star a good place to point our SETI antennas and search for radio signals from an advanced civilization? Group of answer choices No, because such a star (and any planets around it) would not have the heavier elements (carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, etc.) that we believe are necessary to start life as we know it. Yes, because globular clusters are among the closest star clusters to us, so that they would be easy to search for radio signals. Yes, because we have already found radio signals from another civilization living near a star in a globular cluster. No, because such a star would most likely not have a stable (main-sequence) stage that is long enough for a technological civilization to develop. Yes, because such a star is probably old and a technological civilization will have had a long time to evolve and develop there.arrow_forwardHow many Big Macs can fit in the Grand Canyon taking into account gravity and the varying dimensions of the Grand Canyon?arrow_forwardWhat evidence can you cite that the interstellar medium contains both gas and dust? (Select all that apply.) (1)The dust of the interstellar medium can be detected from the emission lines of elements heavier than iron. (2)The dust of the interstellar medium can be detected by the extinction of light from distant stars. (3)The dust of the interstellar medium can be detected by the scattering of blue light from distant or embedded objects. (4)The gas of the interstellar medium can be detected from the radiation of ultraviolet photons. (5)The gas of the interstellar medium can be detected from the radiation of photons of wavelength 21 cm. (6)The gas of the interstellar medium can be detected from the absorption lines present in the light from distant stars, which must be caused by a medium of a density and temperature other than that of the stars emitting the light.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON