
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Suppose you are to measure the BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) removal rate for a primary wastewater treatment plant. You take two samples of raw sewage on its way into the plant and two samples of the effluent leaving the plant. Standard five day BOD tests are run on the four samples with no seeding, producing the following data (See Figure attached)
- Find BOD5 for the raw and treated sewage, and the percent removal of BOD in the treatment plant.
- Find the DO (dissolved oxygen) that would be expected in sample two at the end of the test.
- What would be the maximum volume of treated sewage for Sample 4 that could be put into the 300-mL BOD bottle and still have the DO after five days remain above 2 mg/L?
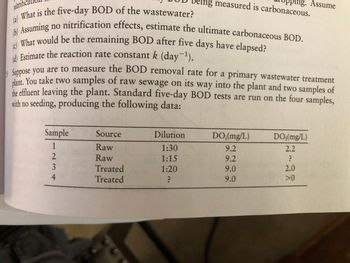
Transcribed Image Text:### Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) Analysis
**Questions:**
(a) What is the five-day BOD of the wastewater?<br>
(b) Assuming no nitrification effects, estimate the ultimate carbonaceous BOD.<br>
(c) What would be the remaining BOD after five days have elapsed?<br>
(d) Estimate the reaction rate constant \(k\) (day\(^{-1}\)).
**Experimental Setup:**
Suppose you are to measure the BOD removal rate for a primary wastewater treatment plant. You take two samples of raw sewage on its way into the plant and two samples of the effluent leaving the plant. Standard five-day BOD tests are run on the four samples, with no seeding, producing the following data:
| Sample | Source | Dilution | DO\(_i\) (mg/L) | DO\(_f\) (mg/L) |
|--------|---------|----------|----------------|----------------|
| 1 | Raw | 1:30 | 9.2 | 2.2 |
| 2 | Raw | 1:15 | 9.2 | ? |
| 3 | Treated | 1:20 | 9.0 | 2.0 |
| 4 | Treated | ? | 9.0 | >0 |
- **Sample Information:**
- **Sample 1**: Raw sewage with a dilution of 1:30. Initial DO is 9.2 mg/L, final DO is 2.2 mg/L.
- **Sample 2**: Raw sewage with a dilution of 1:15. Initial DO is 9.2 mg/L, final DO is unknown.
- **Sample 3**: Treated sewage with a dilution of 1:20. Initial DO is 9.0 mg/L, final DO is 2.0 mg/L.
- **Sample 4**: Treated sewage with undetermined dilution. Initial DO is 9.0 mg/L, final DO is greater than 0 mg/L.
This analysis helps in understanding how effectively the wastewater treatment process reduces the BOD, indicating the level of organic pollutants in the water.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question #5. The fluoride feeder at the Lemieux Island WTP breaks down. As shown below, the well mixed tank flows into a 5 km long distribution pipe. The volume of the tank is 2.5 m³ and the treatment system serves 190 000 people who each use 200 L/d. The rest of the necessary data is provided in the figure. If the fluoride concentration in the tank is 1.0 mg/L when the feed stops, how long until the concentration of fluoride is reduced to 0.01 mg/L at the end of the distribution pipe? Assume that fluoride acts as a conservative substance. Fluoride C = 1.0 mg/L 5 km u = 0.17 m/sarrow_forwardFollowing observations were made on a 4% dilution of wastewater. DO of aerated water used for dilution = 4 mg/1 DO of diluted sample after 5 days of incubation = 0.5 mg/1 DO of original wastewater sample = 0.2 mg/1 What is the value of BOD5 (in mg/1)?arrow_forwardAll information given... Don't say incomplete questionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning