
Microeconomic Theory
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781337517942
Author: NICHOLSON
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
the answer IS NOT A)
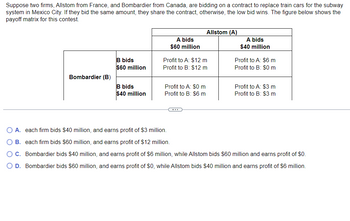
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose two firms, Allstom from France, and Bombardier from Canada, are bidding on a contract to replace train cars for the subway
system in Mexico City. If they bid the same amount, they share the contract, otherwise, the low bid wins. The figure below shows the
payoff matrix for this contest.
Bombardier (B)
B bids
$60 million
B bids
$40 million
A bids
$60 million
Profit to A: $12 m
Profit to B: $12 m
Profit to A: $0 m
Profit to B: $6 m
Allstom (A)
C
A bids
$40 million
Profit to A: $6 m
Profit to B: $0 m
Profit to A: $3 m
Profit to B: $3 m
O A. each firm bids $40 million, and earns profit of $3 million.
B. each firm bids $60 million, and earns profit of $12 million.
O C. Bombardier bids $40 million, and earns profit of $6 million, while Allstom bids $60 million and earns profit of $0.
O D. Bombardier bids $60 million, and earns profit of $0, while Allstom bids $40 million and earns profit of $6 million.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Does each individual in a prisoners dilemma benefit more from cooperation or from pursuing self-interest? Explain briefly.arrow_forwardJane and Bill are apprehended for a bank robbery. They are taken into separate rooms and questioned by the police about their involvement in the crime. The police tell them each that if they confess and turn the other person in, they will receive a fighter sentence. If they both confess, they will be each be sentenced to 30 years. If neither confesses, they will each receive a 20-year sentence. If only one confesses, the they will receive 15 years and the one who stayed silent will receive 35 years. Table 10.7 below represents the choices available to Jane and Bill. If Jane trusts Bill to stay silent, what should she do? If Jane thinks that Bill will confess, what should she do? Does Jane have a dominant strategy? Does Bill have a dominant strategy? A = Confess; B = Stay Silent. (Each results entry lists Janes sentence first (in years), and Bills sentence second.)arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971493Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971493Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305971493
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:9781337794992
Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:9781305156050
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning