
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Don't copy paste old answers pks
Transcribed Image Text:34
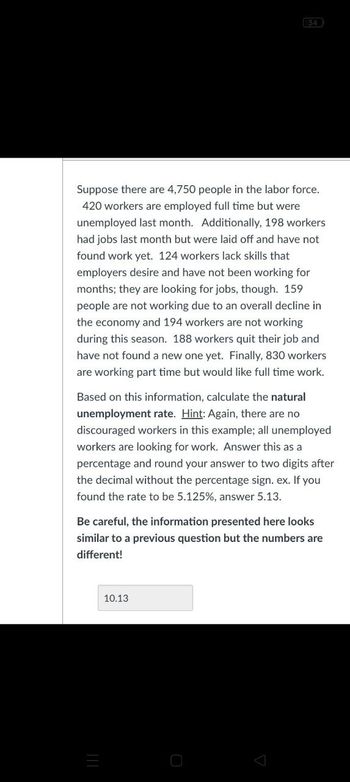
Suppose there are 4,750 people in the labor force.
420 workers are employed full time but were
unemployed last month. Additionally, 198 workers
had jobs last month but were laid off and have not
found work yet. 124 workers lack skills that
employers desire and have not been working for
months; they are looking for jobs, though. 159
people are not working due to an overall decline in
the economy and 194 workers are not working
during this season. 188 workers quit their job and
have not found a new one yet. Finally, 830 workers
are working part time but would like full time work.
Based on this information, calculate the natural
unemployment rate. Hint: Again, there are no
discouraged workers in this example; all unemployed
workers are looking for work. Answer this as a
percentage and round your answer to two digits after
the decimal without the percentage sign. ex. If you
found the rate to be 5.125%, answer 5.13.
Be careful, the information presented here looks
similar to a previous question but the numbers are
different!
10.13
三
О
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- As the cost of energy falls relative to labor in Figure 2-8, and the isocost curve shifts from HJ to FG, firms have an incentive to switch to technology in order to their costs. 4 Tonnes of coal 10 9 8 S 3 2 1 N G Cost-E50 Cost-E40 B F M Cost-E80 H 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Number of workersarrow_forwardquestion part c should contain a grapharrow_forwardHow is MC calculated? 300 for the first MC is incorrect.arrow_forward
- Also write interpretation of answer and give real life example.arrow_forwardMarginal Average Marginal Total Output Price Revenue Total Cost Cost 1 $ 100 $ 100 $ 100.00 $30 2 90 80 63.00 26 80 60 52.67 32 4 70 40 49.50 40 5 60 20 49.60 50 50 50.00 52 7 40 -20 52.29 66 30 -40 55.75 80 20 -60 60.67 100 10 10 -80 67.60 130 Refer to the data for a nondiscriminating monopolist. This firm will maximize its profit by producingarrow_forwardI just went to check my answers for question 4 and 5 on the homework. These questions are based off of the other questions 1-3 that I have already answered. I have answer 4 and 5 but not sure if they are right. I have attached all questions.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education