
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780470458365
Author: Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
The correct answer is 4.394, but I cant understand how to get it...
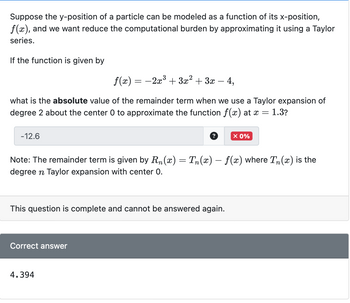
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose the y-position of a particle can be modeled as a function of its x-position,
f(x), and we want reduce the computational burden by approximating it using a Taylor
series.
If the function is given by
f(x) = −2x³ + 3x² + 3x
4,
what is the absolute value of the remainder term when we use a Taylor expansion of
degree 2 about the center 0 to approximate the function f(x) at x = 1.3?
-12.6
Note: The remainder term is given by Rn(x) = Tn(x) − ƒ(x) where Tɲ(x) is the
degree n Taylor expansion with center 0.
This question is complete and cannot be answered again.
Correct answer
X 0%
4.394
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 1 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Simplify the following... 27 2/3 32 4/5arrow_forwardUsing the Definition of am/n Simplify:a. 272/3 b. 93/2 c. 81-3/4.arrow_forwardprocess. 530.16682543 Jump to level 1 Let U2 be a basis for a subspace of IR2X2 12 the Gram-Schmidt process to find an orthogonal pasis under the Frobenjus inner product. 1.38 Orthogonal basis Ex: 5 b= Ex 5 4. Checkarrow_forward
- why u picked x=139? is there any reason? if this is exam question, apparently I dont have time to list all the possible values of x and figure out 139.arrow_forwardHi, could you please do question 7 with letters b, c, and d.arrow_forwardGiven P(A) = 0.21, P(B) = 0.40, P(A or B) = 0.35, what is P(A and B)? Answer in decimal form. Round to 2 decimal places as needed. Your Answer:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780073397924
Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781118141809
Author:Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

