
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please solve the second image. *First image is for information only.
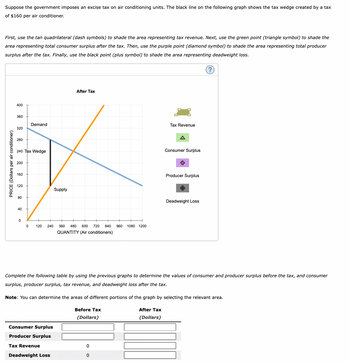
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose the government imposes an excise tax on air conditioning units. The black line on the following graph shows the tax wedge created by a tax
of $160 per air conditioner.
First, use the tan quadrilateral (dash symbols) to shade the area representing tax revenue. Next, use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade the
area representing total consumer surplus after the tax. Then, use the purple point (diamond symbol) to shade the area representing total producer
surplus after the tax. Finally, use the black point (plus symbol) to shade the area representing deadweight loss.
PRICE (Dollars per air conditioner)
400
360
320
280
240 Tax Wedge
200
160
120
80
40
Demand
0
0 120 240 360 480 600 720 840 960 1080 1200
QUANTITY (Air conditioners)
Supply
Consumer Surplus
Producer Surplus
After Tax
Tax Revenue
Deadweight Loss
Tax Revenue
Complete the following table by using the previous graphs determine the values of consumer and producer surplus before the tax, and consumer
surplus, producer surplus, tax revenue, and deadweight loss after the tax.
Consumer Surplus
Note: You can determine the areas of different portions of the graph by selecting the relevant area.
Before Tax
(Dollars)
After Tax
(Dollars)
0
0
Producer Surplus
Deadweight Loss
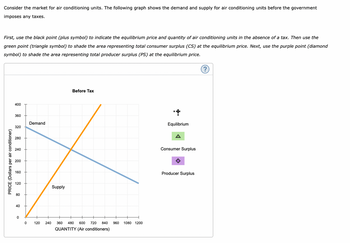
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the market for air conditioning units. The following graph shows the demand and supply for air conditioning units before the government
imposes any taxes.
First, use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the equilibrium price and quantity of air conditioning units in the absence of a tax. Then use the
green point (triangle symbol) to shade the area representing total consumer surplus (CS) at the equilibrium price. Next, use the purple point (diamond
symbol) to shade the area representing total producer surplus (PS) at the equilibrium price.
PRICE (Dollars per air conditioner)
400
360
320
280
240
200
160
120
80
40
0
0
Demand
120 240
Supply
Before Tax
360 480 600 720 840 960 1080 1200
QUANTITY (Air conditioners)
+
Equilibrium
A
Consumer Surplus
Producer Surplus
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardHayfever Farms is an 80‑acre hay farm in Colorado. Due to the legalization of marijuana production in the state, the owners are considering changing the farm's name to Blissful Acres and growing marijuana instead of hay. Use the information presented in the table to answer three questions. Number of acres MC $ MR $ (hay) MR $ (marijuana) 10 320 730 5,600 20 200 730 5,600 30 540 730 5,600 40 730 730 5,600 50 1,200 730 5,600 60 3,200 730 5,600 70 5,600 730 5,600 80 6,700 730 5,600 If they continue to grow only hay, how many acres should Hayfever Farms devote to growing hay in order to maximize profits? area devoted to hay:_______ acres If the owners decide to only grow marijuana, how many acres should Blissful Acres devote to growing marijuana in order to maximize profits? area devoted to marijuana:_______ acres Which outcome likely happens due to the legalization of marijuana production and consumption? The number of growers…arrow_forwardA group of participants was surveyed and the information collected shown in the partially completed contingency table below regarding the site of skin cancer. Firstly, calculate the missing values. Melanoma Other Total Head U 43 X Trunk 52 V 98 Extremities 142 112 Y Total 229 W Z Now, using the completed contingency table, select the statements from the following list that are true. Note: a statement is true only if the value you calculated from the completed contingency table, when rounded to the same number of decimal places as in the statement, is the same as the value in the statement. 18.1% of skin cancers appear on the head 71.4% of skin cancers were melanomas or appeared on the head Given the skin cancer is something other than melanoma, the probability it is not on the extremities is 0.443 Of skin cancers appearing on the trunk, 46.9% are not melanomasarrow_forward
- Greenhouse gases trap heat and make the planet warmer. Human activities are responsible for almost all of the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere over the last 150 years. In this part, you will draw two pie graphs. A pie graph is used to show how a certain quantity has been divided into several parts, as well as to show the comparisons among these parts. 1. The data table below shows the total U.S. greenhouse gas emissions by economic sector in 2013, in million metric tons of CO2. On the pie graph provided, complete the graph to show the percent of greenhouse gas emissions for each economic sector. Label each section of the pie graph with its economic sector. The percent for "Agriculture" has been drawn and labeled for you. Economic Sector Electricity Transportation Industry Commercial & Residential Agriculture Percent of Greenhouse Gas Emissions 31 27 21 12 9 80 75 70- 85 65 95 90 wlad Percent 0 100 Agri- culture 55 50 45 10 40 35 20 25 30arrow_forwardplease answer the questions on the image attached with work shown, thanks!arrow_forwardIs there any graph that can support this answer?arrow_forward
- Consider the following data: −9,13,−14,−14,−9,−14,−9−9,13,−14,−14,−9,−14,−9 Copy Data Step 3 of 3: Calculate the value of the range.arrow_forwardUse graphical method to solve the following LPP: Maximise Z = x +4y Subject to the constraints: x + y < 1 2x + 2y 2 4 *2 0, y 2 0arrow_forwardGiven the functional relationship: y = 14x5/x2 find the value of y when x = 1.5arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education