
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
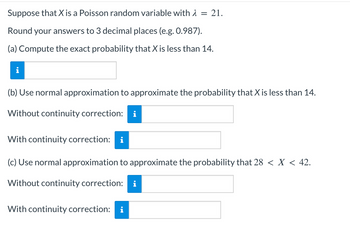
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that X is a Poisson random variable with λ = 21.
Round your answers to 3 decimal places (e.g. 0.987).
(a) Compute the exact probability that X is less than 14.
(b) Use normal approximation to approximate the probability that X is less than 14.
Without continuity correction:
With continuity correction:
(c) Use normal approximation to approximate the probability that 28 < X < 42.
Without continuity correction: i
With continuity correction: i
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 18 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Say we have a continuous random variable X. Let f(x) = 3x² for support =[0,1]. What is P(X>0.75|X>0.5), probability X is greater than 0.75 given X is greater than 0.5? Round to the nearest 2nd decimal place, x.xxarrow_forwardUnanswered a Save (%-D) #3 Insurance C An insurance company sold 8,000 policies ($100,000 payout value) this year. The probability of death for each person has been determined to be .002. The company charges $225 for each policy. Use the Poisson approximation to determine P(They lose $300,000 or more) Type your numeric answer and submit Unanswered HSavearrow_forwardLet X represent a continuous random variable with a Uniform distribution over the interval from 0 to 2. Find the following probabilities (use 2 decimal places for all answers):(a) P(X ≤ 0.22) = (b) P(X < 0.22) = (c) P(0.98 ≤ X ≤ 1.92) = (d) P(X < 0.98 or X > 1.92) =arrow_forward
- When a man observed a sobriety checkpoint conducted by a police department, he saw 656 drivers were screened and 5 were arrested for driving while intoxicated. Based on those results, we can estimate that P(W)equals=0.00762,where W denotes the event of screening a driver and getting someone who is intoxicated. What does P(W) denote, and what is its value? What does P(W) represent? P(W)=arrow_forwardLet X ~ Geom(p), a geometric distribution with parameter p € (0, 1). This is a discrete probability distribution on the positive integers, with p.m.f. given by fx (k) = (1 − p)k-¹p, k = = 1, 2,... (i) Verify (by calculation) that the log-likelihood function for the parameter p is given by l(x;p) = n (logp + (x − 1) log(1 − p)). - (ii) Derive the MLE estimator for p, and use it to compute the MLE estimate for the following sample data ¹: 1 3 1 1 1 2 3 1 1 1 1 (iii) What is the MLE estimator for 1/p? Verify this estimator is unbiased.arrow_forwardLet X equal the IQ of a randomly selected American. Assume X ~ N( μ μ {"version":"1.1","math":"μ"} =100, σ σ {"version":"1.1","math":"σ"} =4). What is the probability that a randomly selected American has an IQ below 90?arrow_forward
- Suppose you repeatedly flip a fair coin. Use the normal approximation discussed above to (approximately) compute the probability that it takes more than 210 flips to get 100 heads (you should use the continuity correction). The coin is unfair with probability of observing a head being 1/3. Suppose you repeatedly flip this unfair coin. Use the normal approximation discussed above to (approximately) compute the probability that it takes more than 210 flips to get 60 heads (you should again use the continuity correction).arrow_forwardCompute P(X) using the binomial probability formula. Then determine whether the normal distribution can be used to estimate this probability. If so, approximate P(X) using the normal distribution and compare the result with the exact probability. n=56 p=0.5 x=30 A)For n=56, p=0.5, and X=30, use the binomial probability formula to find P(X). B)Can the normal distribution be used to approximate this probability? A. No, because np(1−p)≤10 B. Yes, because np(1−p)≥10 C. Yes, because np(1−p)≥10 D. No, because np(1−p)≤10 C) Approximate P(X) using the normal distribution. Use a standard normal distribution table. A. P(X)=enter your response here (Round to four decimal places as needed.) B. The normal distribution cannot be used. D) By how much do the exact and approximated probabilities differ? A.enter your response here (Round to four decimal places as needed.) B. The normal distribution cannot be used. E)By…arrow_forwardShow that the expectation of the exponential distribution with param- eter A is 1/A.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman