
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134753119
Author: Sheldon Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
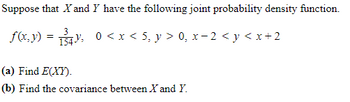
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that X and Y have the following joint probability density function.
f(x,y) = 134² 0 < x < 5, y > 0, x − 2 < y < x+2
(a) Find E(XY).
(b) Find the covariance between X and Y.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Let X be a random variable with probability density function 3 f(x) = ,a², –1 < = <1 2 Which of the following is the probability density function of Y = X – 1?arrow_forwardSuppose that X and Y have a joint probability density function given by ce-3z=5y if a, y 20 fx.y(T, y) = otherwise Find the marginal probability density function fx and state the name of the distribution of X.arrow_forward(16) Let f (x) = e¯t if t ≥ 0 and ƒ (t) = 0 if t < 0. (a) Show that f is a probability density function. (b) Find P(2 ≤ X ≤ 6.arrow_forward
- Only need (b), thank youarrow_forwardSuppose that X and Y have the following joint probability density function.f (x, y) = 3x 400 0 < x < 6, y > 0, x − 4 < y < x + 4 (a) Find E(XY). (b) Find the covariance between X and Y.arrow_forwardSuppose that the random variables X and Y have the following joint probability density function. f(x, y) = ce-6x-2y, 0 < y < x. (a) Find the value of c. (b) Find P(X < Y < 2) ,arrow_forward
- [1] The joint probability density function of two continuous random variables X and Y is sc, 0arrow_forwardLet X denote 0.025 × the ambient air temperature (˚C) and let Y denote the time (min) that it takes for a diesel engine to warm up. Assume that (X, Y) has joint probability density function f(x,y) = 1.6x (1 − x)(6 + 5x − 4y), for 0 < x < 1, 0 < y < 0.5. While you cannot guess the value of the correlation from the regression curve for X or Y, do they suggest whether it likely is positive or negative?arrow_forward2. Let the joint probability density function of continuous random variables X and Y be given by Find fx|y(x|y). f(x, y) = 2 if 0 < x < y < 1 elsewhere.arrow_forward
- Suppose that X and Y have a joint probability density function given by Sce-32-5y if r, y 2 0 fx.x(r, y) = otherwise (a) Determine the value of the normalization constant c. (b) Find the marginal probability density function fx and state the name of the distribution of X. (c) Find the conditional probability density function fy|x=z•arrow_forward1. Consider the two functions ƒ(x) = C(2x − x³), g(x) = C(2x − x²), 0 < x < 2. (1) Could f be a probability density function? If so, determine C. If not, explain the reason that why f is not a probability density function. 0 < x < 2, (2) Could g be a probability density function? If so, determine C. If not, explain the reason that why g is not a probability density function.arrow_forwardLet X be a random variable with probability density function [ a + bx², 0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:PEARSON
