
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
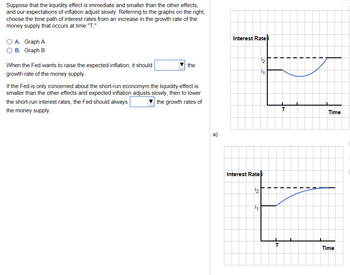
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that the liquidity effect is immediate and smaller than the other effects,
and our expectations of inflation adjust slowly. Referring to the graphs on the right,
choose the time path of interest rates from an increase in the growth rate of the
money supply that occurs at time "T."
A. Graph A
B. Graph B
When the Fed wants to raise the expected inflation, it should
growth rate of the money supply.
the
If the Fed is only concerned about the short-run economym the liquidity effect is
smaller than the other effects and expected inflation adjusts slowly, then to lower
the short-run interest rates, the Fed should always
the money supply.
the growth rates of
a)
Interest Rate i
¹2
1₁
Interest Rate i
¹2
I
+
T
1
I
I
I
I
T
1
1
T
T
I
I
I
1
1
Time
Time
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the tradeoff that the Fed faces in the short run? In the short run, the Fed faces a tradeoff between ________. A. the nominal interest rate and the real interest rate B. monetary aggregates and credit aggregates C. short-term interest rates and long-term interest rates D. inflation and unemploymentarrow_forwardJapan's money supply is growing rapidly at a 5.54% while real GDP is increasing at 8.29%. Japan's real interest rate is also growing at 4.46%. *we are assuming Quantity Theory of Money, Classical Dihotomy, and Fisher Effect effect are true. a. calculate the inflation rate b. calculate nominal interest rate c. calculate GDP growth ratearrow_forwardBeing aware of the Federal Reserve's monetary policy and how it can affect interest rates can impact planning for major purchases. When interest rates rise the Federal Reserve is combating. and makes it expensive to finance a car or a home loan. unemployment; more unemployment; less inflation; more inflation; less O O hparrow_forward
- The Fed is most likely to raise the federal funds rate target when the Fed expects _______. A. high unemployment and a recessionary gap B. high long-term interest rates and a recessionary gap C. low unemployment and an inflationary gap D. banks to hold ample reserves and charge low interest rates on loansarrow_forwardTyped plzzz and Asap Thanksarrow_forwardeconomic Illustrate each of the following situations with a graph showing the IS curve and the Fed rule, and explain what happens to the equilibrium values of the interest rate and output: a. An increase in G with the money supply held constant by the fed b. A decrease in Z with no change in Government soending PLEASE SHOW GRAPHarrow_forward
- Question 7. Suppose there is an exogenous increase in the price of oil in an economy. a. Use the aggregate demand and supply model to illustrate and examine the impact of the oil-price increase on output, employment and the price level in both the short run and the long run. b. If the Bank of Canada cares about keeping output and employment at their natural-rate levels, what is the policy response of the Bank of Canada? What is the impact of policy response on the price level? Use the aggregate demand and supply model to explain your answer. Please illustrate the answers using figures with aggregate demand and supply curves. Please also briefly explain the answers in words.arrow_forwardI would like to ask how to calculate c and darrow_forwardThe Fed is fighting recession and it happens to overstimulate the economy. If the expected inflation rate rises above the 2 percent goal, what is the cost of returning the inflation rate back to its goal? The cost of returning the inflation rate back to its goal is _______. A. an inflationary gap and an even higher inflation rate than initially B. unemployment below the natural unemployment rate C. a decrease in potential GDP and aggregate supply D. a recessionary gap and a higher unemployment ratearrow_forward
- . What is the opportunity cost of holding money? How is k related to the velocity of money? s. Use the Quantity Theory of Money to explain how long run inflation occurs. If the Federal Reserve Bank wishes to keep the inflation rate at zero percent, at what rate should the money supply grow? Why?arrow_forwardF2 3 E D #3 1.7 The hypothetical information in the table below shows what the values for real GDP and the price level would have been in 2019 if the Federal Reserve did not use monetary policy: Real GDP F3 Year 2018 2019 b) Suppose t ZUTA If the Fed wanted to keep real expansionary pol R LL F h Real GDP Full employment real GDP The inflation rate d. The unemployment rate F4 I Potential Real GDP $18.5 trillion 19.0 trillion c) Draw an aggregate demand and aggregate supply graph to illustrate your answer. Be sure that your graph contains LRAS curves for 2018 and 2019; SRAS curves 2018 and 2019; AD curve for 2018 and 2019, with and without monetary policy actions; and equilibrium real GDP and the price level in 2019 with and without policy. DII % 5 T G F5 O Search 6 F6 Y $18.5 trillion 19.4 trillion H J F7 in real GDP at its potential EDC & 7 U PrtScn F8 Price Level *00 142 150 8 t have u Home F9 K 9 End O F10 0 PgUp F11 Parrow_forwardWhat happens when a central bank pursues inflation targeting? A. The policy actions that central banks use to achieve the inflation target are kept secret. B. With inflation targeting, the United States would be more successful at achieving low and stable inflation. C. Many central banks achieve their inflation target at the expense of extremely high unemployment. D. The bank announces an explicit inflation target and the public is confident the bank's policy will achieve that target. thank you!!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education