
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
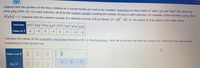
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that the genders of the three children of a certain family are soon to be revealed. Outcomes are thus triples of "girls" (g) and "boys" (b), which we write gbg, bbb, etc. For each outcome, let R be the random variable counting the number of boys in each outcome. For example, if the outcome is gbg, then R(gbg) = 1. Suppose that the random variable X is defined in terms of R as follows: \( X = 2R^2 - 2R - 4 \). The values of X are given in the table below.
| Outcome | gbb | bgg | bbg | ggb | bgb | gbg | ggg |
|---------|-----|-----|-----|-----|-----|-----|-----|
| Value of \( X \) | 0 | -4 | 0 | -4 | 8 | 0 | -4 | -4 |
Calculate the values of the probability distribution function of X, i.e., the function \( p_X \). First, fill in the first row with the values of X. Then fill in the appropriate probabilities in the second row.
Below the text, there's a diagram divided into blocks where the value \( x \) of \( X \) is displayed as a question mark placeholder, and a row below awaiting the insertion of the probabilities \( p_X(x) \). The specific probability boxes are unfilled, allowing for completion.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1

Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A psychologist found a study which claiming that 32% of patients who visit a psychologist have symptoms of anxiety. This psychologist had 44 patients visit. Let x = the number of patients that had symptoms of anxiety. (a) The random variable is which of the following? O the number of psychologists O the number of patients who visited the psychologist the number of patients who had symptoms of anxiety O the number of patients without symptoms of anxiety (b) How many total patients did the psychologist have visit?arrow_forwardA vaccine has a 90% probability of being effective in preventing a certain disease. The probability of getting the disease if a person is not vaccinated is 50%. In a certain geographic region, 25% of the people get vaccinated. If a person is selected at random, what is the probability that he or she will contract the disease?arrow_forwardThe genotype of an organism can be either normal (wild type, W) or mutant (M). Each generation, a wild type individual has probability 0.03 of having a mutant offspring, and a mutant has probability 0.005 of having a wild type offspring.arrow_forward
- If you have a sample of 100 patients at a hospital and 20 of them have the flu, what is the probability Of randomly selecting 3 patients in a row who have the flue?arrow_forwardI will be glad if the answer comes quicklyarrow_forwardAn ordinary (fair) coin is tossed 3 times. Outcomes are thus triples of "heads" (h) and "tails" (t) which we write hth, ttt, etc. For each outcome, let R be the random variable counting the number of heads in each outcome. For example, if the outcome is tth, then =Rtth1. Suppose that the random variable X is defined in terms of R as follows: =X−R2−3R4. The values of X are given in the table below. Outcome htt tht hth thh ttt hhh hht tth Value of X −6 −6 −6 −6 −4 −4 −6 −6 Calculate the values of the probability distribution function of X, i.e. the function p X. First, fill in the first row with the values of X. Then fill in the appropriate probabilities in the second row.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman