
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
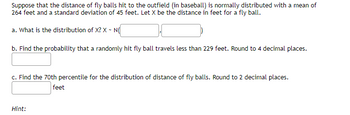
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that the distance of fly balls hit to the outfield (in baseball) is normally distributed with a mean of
264 feet and a standard deviation of 45 feet. Let X be the distance in feet for a fly ball.
a. What is the distribution of X? X ~ N(
b. Find the probability that a randomly hit fly ball travels less than 229 feet. Round to 4 decimal places.
c. Find the 70th percentile for the distribution of distance of fly balls. Round to 2 decimal places.
feet
Hint:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Assume the selling prices of homes in a particular community follow a normal distribution with a mean of $263,100 and a standard deviation of $43,200. Complete parts a through c. a. Determine the range of selling prices in this community that includes one standard deviation around the mean. The range is from $ to $ (Type integers or decimals. Use ascending order.) b. Determine the range of selling prices in this community that includes two standard deviations around the mean. The range is from $ to $ (Type integers or decimals. Use ascending order.) c. Determine the range of selling prices in this community that includes three standard deviations around the mean. The range is from $ to $1. (Type integers or decimals. Use ascending order.)arrow_forwardAssume that adults have IQ scores that are normally distributed with a mean of u= 105 and a standard deviation o = 15. Find the probability that a randomly selected adult has an IQ between 91 and 119. Click to view page 1 of the table. Click to view page 2 of the table. ces The probability that a randomly selected adult has an IQ between 91 and 119 is (Type an integer or decimal rounded to four decimal places as needed.) Exp The usearrow_forwardAssume that adults have IQ scores that are normally distributed with a mean of u= 100 and a standard deviation g= 15. Find the probability that a randomly selected adult has an IQ less than 118. Click to view page 1 of the table. Click to view page 2 of the table. The probability that a randomly selected adult has an IQ less than 118 is (Type an integer or decimal rounded to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- Assume that the readings at freezing on a batch of thermometers are normally distributed with a mean of 0°C and a standard deviation of 1.00°C. A single thermometer is randomly selected and tested. Find P30, the 30-percentile. This is the temperature reading separating the bottom 30% from the top 70%.P30 = °C(Round answer to three decimal places)arrow_forwardFind the area of the shaded region. The graph to the right depicts IQ scores of adults, and those scores are normally distributed with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. Click to view page 1 of the table. LOADING... Click to view page 2 of the table. LOADING... 90 A graph with a bell-shaped curve, divided into 2 regions by a vertical line. The vertical line extends from the bell curve to the x-axis, and is located on the left half, under the curve. The region on the left of this line is shaded. The x-axis below the vertical line is labeled 90. Question content area bottom Part 1 The area of the shaded region is enter your response here. (Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardThe ratings of applicants for credit are normally distributed with a mean of 200 and a standard deviation of 50. Find the 60th. percentile, the rating score that separates the lower 60% from the top 40%. Round to the nearest integer. a. 208 b. 187 c. 211 d. 213arrow_forward
- Assume that a randomly selected subject is given a bone density test. Those test scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. Find the probability that a given score is between -2.05 and 3.87 and draw a sketch of the region. Sketch the region. Choose the correct graph below. OA. OB. OC. OD. -2.05 3.87 2.05 3.87 -2.05 3.87 -2.05 3.87 The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardAssume that adults have IQ scores that are normally distributed with a mean of μ = 105 and a standard deviation o=20. Find the probability that a randomly selected adult has an IQ between 88 and 122. Click to view page 1 of the table. Click to view page 2 of the table. The probability that a randomly selected adult has an IQ between 88 and 122 is (Type an integer or decimal rounded to four decimal places as needed.) Carrow_forwardAssume that the heights of women are normally distributed with a mean of 63.6 inches and a standard deviation of 2.5 inches. If 100 women are randomly selected, find the probability that they have a mean height greater than 63.0 inches. O A. 0.0082 O B. 0.8989 O C. 0.2881 O D. 0.9918 Next View Instructor Tip Calculator 809 PM 70°F Cloudy 10/8/2021 33 2 Type here to search 10/05/17 PrtSc Insert Delete AI F9 F10 F11 F12 F7 F8 F5 F6 Esc F3 F4 F1 & Backspace Num Lock C@ %23 5 7 080 3 T. Y కాం Home C Tab H. K Enter G A CapsLk 1 Shift C V N End hift PgUp Alt Ctrl End + |/ A MI 小 44arrow_forward
- Compute the standard deviation of the sampled proportions if p=.8 and n=50. Round to three places.arrow_forwardFind the area, square unit, to the nearest thousandth of the standard deviation between the given z-scores. Z equals 1.12 and z equals 1.73.arrow_forwardListed in the data table are IQ scores for a random sample of subjects with medium lead levels in their blood. Also listed are statistics from a study done of IQ scores for a random sample of subjects with high lead levels. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations. Do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. Click the icon to view the data table of IQ scores. a. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the mean IQ scores for subjects with medium lead levels is higher than the mean for subjects with high lead levels. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? Assume that population 1 consists of subjects with medium lead levels and population 2 consists of subjects with high lead levels. X A. Ho: H₁ H₂ H₁ H₁ H₂ c. Ho: M₁ = H₂ H₁: H₁ H₂ The test statistic is 0.56. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The P-value is (Round to three decimal…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman