
Microeconomic Theory
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781337517942
Author: NICHOLSON
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
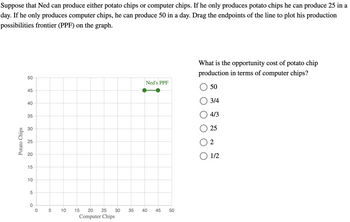
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that Ned can produce either potato chips or computer chips. If he only produces potato chips he can produce 25 in a
day. If he only produces computer chips, he can produce 50 in a day. Drag the endpoints of the line to plot his production
possibilities frontier (PPF) on the graph.
Potato Chips
50
45
64
40
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
0
What is the opportunity cost of potato chip
production in terms of computer chips?
Ned's PPF
50
3/4
4/3
25
LQ
5
10
15 20 25 30
35 40
40
Computer Chips
45
50
2
○ 1/2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Why is a production possibilities frontier typically drawn as a curve, rather than a straight line?arrow_forwardEmily buys an air conditioner that costs $700. Because the air in her home is cleaner, its use saves her $250 in curtain cleaning costs over the lifetime of the air conditioner. In money terms, what is the opportunity cost of the air conditioner?arrow_forwardWhat is Maries opportunity cost of purchasing a pie?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning


Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning



Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:OpenStax

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506893
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:Cengage Learning