
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Suppose that a new free trade agreement allows the economy to import cheaper goods from overseas, thereby decreasing the general price level.
Adjust the following graph by either shifting the consumption function curve or the initial point on the consumption function curve (A) to illustrate the impact of a fall in the price level.
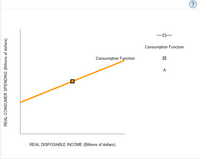
Transcribed Image Text:(?
Consumption Function
Consumption Function
A
REAL DISPOSABLE INCOME (Billions of dollars)
REAL CONSUMER SPENDING (Billions of dollars)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If the price level increases, what happens to the consumption function? Why?arrow_forwardKindly solve this correctlyarrow_forward3. Suppose that you are interested in answering the question of how consumption reacts to tax increases. In recent years, government has imposed tax increases to fund increased infrastructure spending. If you could design an ideal experiment to answer this question, how would you do so? Do you think it would be practical to use this experiment on a large scale?arrow_forward
- Show full answers to the questions and steps to this exercisearrow_forward1a) and b)arrow_forwardThe figure below shows the average share of total household expenses for a good and the inflation-adjusted price of the same good. The share of all expenses line is calculated as expenditures on this good (that is the price of this good multiplied by the quantity of this good purchased) divided by total household expenses. This line shows how expenditures on this good changes over time, holding total spending constant. The other line is the price of this good adjusted for inflation (i.e., the increase in the price level for all goods). The specific units are obscured on purpose. Use these data to characterize the price elasticity of demand. Explain using the definitions of price elasticity of demand and total expenditure. Notice that I am not asking you to calculate the price elasticity of demand. Use the data to talk about the size of price elasticity of demand in general terms. Is demand elastic or inelastic? Is the price elasticity of demand very large? Very small? Close to 1?…arrow_forward
- Consider a closed economy that is characterized by the following equations: Y = C +1+ G (1) C = 500 + 0.75(Y-T) (2) | = 375-25r (3) T = 500 (4) G = 500 (5) m = m, (6) m. = 1000 (7) m, = 0.5Y (8) m, = -50r (9) Where Y is the GDP, C is private consumption expenditure, I is the Investment expenditure, G is government expenditure, T is tax revenues, M̟ is money supply, M, is transaction demand for money. M, is the speculative demand for money and r is the interest rate (in % points). a) Derive (m/P) the demand for real money balances equation (where P is the aggregate price level.) b) Derive the IS and LM equations of the economy (Express Y as a function of r and assume Pis fixed at 1.0.) c) Calculate the short-run equilibrium values of Y and r in the economy.arrow_forwardSuppose that M = 2000 and that k = 2. What is the price level P at which the economy is in long-run- equilibrium? Plot such an equilibrium on a diagram with P on the vertical axis and Y on the horizontal axis, by distinguishing between the short-run and the long-run equilibrium.arrow_forward1. What is a market-clearing model? When is it appropriate to assume that market clear? 2. Use the model of supply and demand to explain how fall in the price of frozen yogurt would affect the price of ice cream and the quantity of ice cream sold. In your explanation, identify the exogenous and endogenous variables. 3. Consider an economy that produces and consumes hot dogs and hamburgers. In the following table are data for two different years. Goods Hot dogs Hamburgers Quantity (2010) 200 200 Price (2010) $2 $3 Quantity (2020) 250 250 Price (2020) $4 $4 Using 2010 data as the base year Compute the following statistics for each year. Nominal GDP, Real GDP, GDP Deflator, Inflation rate using GDP deflator, CPI, Inflation rate using CPI. (Hint: i) to calculate CPI use base year fixed quantity Hot dogs 200 and Hamburgers 200, ii) To calculate inflation rate, use percentage change in price level between two years.)arrow_forward
- Suppose Bank of England is considering using the tool of cutting interest rates to boost household consumption. In this question you will be asked to use the intertemporal choice model to assess the impact of different policies on household consumption. Suppose a consumer's current income is £25,000 and their future income is £30,000, and they initially face a market interest rate of 15% on both saving and borrowing. (a) In a diagram with consumption this year (C1) on the horizontal axis and consumption next year (C2) on the vertical axis, illustrate this consumer's budget constraint (using the numerical values set above) and indicate their optimal choice by drawing a indifference curve convex to the origin, assuming that at the current interest rate it is optimal for them to save. (b) Calculate (using the numerical values set above) and interpret their marginal rate of time preference at their optimal choice. (c) Illustrate and explain how a fall in the market interest rate from 15%…arrow_forward1. Which of the following equations is the correct expression of the IS curve? ao+Bo-B₁i+G a. Y = b. Y= C. d. Y= 1-α₁ (1-t) C+I+G Y = 1-a₁ (1-1) ao+Bo-B₁i+G 1+α₁ (1-t) C+I+G 1+a₁ (1-1)arrow_forwardThe table below shows the parameters for the economy of Hutu. Give your answers to one decimal point. XN = 160 0.15Y G = 220 C = 40 + 0.65Y I = 150 a. The value of equilibrium income is $ b. If exports were to increase by 40, the new value of equilibrium income would be $ c. Given your answer in part (b), the new value for XN is $ d. Given the equilibrium income in part (a), if full employment income is $800, what change in government spending is necessary to move the economy to this level? Government spending needs to decrease by $. Aarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education