
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
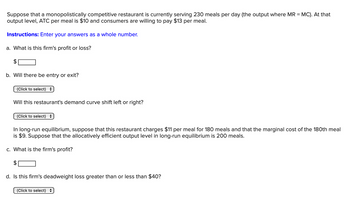
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that a monopolistically competitive restaurant is currently serving 230 meals per day (the output where MR = MC). At that
output level, ATC per meal is $10 and consumers are willing to pay $13 per meal.
Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number.
a. What is this firm's profit or loss?
b. Will there be entry or exit?
(Click to select) =
Will this restaurant's demand curve shift left or right?
(Click to select) =
In long-run equilibrium, suppose that this restaurant charges $11 per meal for 180 meals and that the marginal cost of the 180th meal
is $9. Suppose that the allocatively efficient output level in long-run equilibrium is 200 meals.
c. What is the firm's profit?
d. Is this firm's deadweight loss greater than or less than $40?
(Click to select) +
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose that an monopolistically competitive restaurant is currently serving 270 meals per day (the output where MR = MC). At that output level, ATC per meal is $10 and consumers are willing to pay $13 per meal. What is the size of this firm's profit or loss? Profit of $ Will there be entry or exit? Entry k Will this restaurant's demand curve shift left or right? Left In long-run equilibrium, suppose that this restaurant charges $11 per meal for 180 meals and that the marginal cost of the 180th meal is $9. ices What is the size of the firm's profit? $ MacBook Airarrow_forwardFill in the missing data for this Monopolistically Competitive firm. Don't forget to answer the questions below the chart. I. Average Total Marginal Total Marginal Total Total Quantity Price Revenue Revenue Cost Cost Cost Profit 50 na na -50 1 48 75 2 46 45 37 4 31 135 25 15 32 38 7 175 253 /////// 8. 144 311 9 90 379 /////I/ 10 459 This firm's fixed costs are? Assuming no inflation, we would predict this firm's price to rise/fall/ stay the same. Explain your answer.arrow_forwardSuppose that a monopolistically competitive restaurant is currently serving 230 meals per day (the output where MR = MC). At that output level, ATC per meal is $10, and consumers are willing to pay $12 per meal. What is this firm's profit or loss? Will there be entry or exit? Will this restaurant's demand curve shift left or right? In long-run equilibrium, suppose that this restaurant charges $11 per meal for 180 meals and that the marginal cost of the 180th meal is $8. What is the firm's profit? (LO3)arrow_forward
- solve botharrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Increasing Returns to Scale and Monopolistic Competition Starting from the long-run trade equilibrium in the monopolistic competition model, as illustrated in the accompanying figure, consider what happens when industry demand D increases. For instance, suppose that this is the market for cars, and lower gasoline prices generate higher demand D. a. Show the resulting shift in the D/NT, d, and mr curves. Assume the price increases to $13. Place point A on the new short-run equilibrium. Price 09876 20 19 18 17 16 15 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 mr D/NT d A • AC MC 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Quantityarrow_forwardplease helparrow_forward
- Mm.44. Subject:- Economyarrow_forwardAssume that in short-run equilibrium, a particular monopolistically competitive restaurant (Applebee's) charges $12 for each order of Chicken Parmesan and sells 52 orders per day. The average total cost (ATC) for those 52 orders is $10. How much revenue will the firm take in each day? $ What will be the firm's economic profit or loss on Chicken Parmesan? Next, suppose that other restaurants add/remove chicken parmesan from their menus (entry or exit occurs) and a long-run equilibrium is established. If the Applebees daily Chicken Parmesan orders remain at 52 units, what price will it be able to charge? $ What will be its economic profit or loss?arrow_forward5- 3- 1- 20 40 60 80 100 Q MR Using the above graph, This profit-maximizing firm will produce Blank 1 units. -MC What price will this profit-maximizing firm charge? $Blank 2 (Do NOT enter the '$' in your response. Enter only the whole dollar amount; do NOT enter cents.) If the industry was perfectly competitive instead of monopolistic, then market output would be Blank 3 units and market price would be $Blank 4. (Do NOT enter the '$' in your response. Enter only the whole dollar amount; do NOT enter cents.) Blank 1 Blank 2 Blank 3 Blank 4 Add your answer Add your answer Add your answer Add your answerarrow_forward
- Explain the difference in market power between perfectly competitive firms and monopolistically competitive firms. Which firms have more control over prices and/or output? Why? What are some industry examples of each type of market structure?arrow_forwardMail - Oliver, Ak X 13) Online Quiz i heducation.com/ext/map/index.html?_con=con&external_browser=0&launchUrl=https%253A%2525 1er. Excel Module 8 X 13 10 Refer to the graph for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This f 0 100 X M Question 16-LCX M Inbox (9,354) - Multiple Choice lass of $280 MC 160 180 210 Quantity ATC MR Darrow_forward2. A ski resort faces daily demand given by p = a - Q, where a varies from day to day. Over a three- day period, a takes on the values 80.100, and 120. The marginal cost is zero. The fixed cost for the three-day period is $2500. If the firm uses dynamic pricing, it changes its price every day to maximize profit. If it uses non-dynamic pricing, it sets the same price for all three days, assuming that a takes on its average value of 100 each day. Calculate the consumer surplus and the firm's profit over the three-day period under each pricing approach.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education